Tuberculosis among health care workers
- PMID: 21392441
- PMCID: PMC3298382
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1703.100947
Tuberculosis among health care workers
Abstract
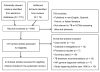
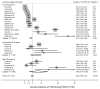
To assess the annual risk for latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) among health care workers (HCWs), the incidence rate ratio for tuberculosis (TB) among HCWs worldwide, and the population-attributable fraction of TB to exposure of HCWs in their work settings, we reviewed the literature. Stratified pooled estimates for the LTBI rate for countries with low (<50 cases/100,000 population), intermediate (50-100/100,000 population), and high (>100/100,000 population) TB incidence were 3.8% (95% confidence interval [CI] 3.0%-4.6%), 6.9% (95% CI 3.4%-10.3%), and 8.4% (95% CI 2.7%-14.0%), respectively. For TB, estimated incident rate ratios were 2.4 (95% CI 1.2-3.6), 2.4 (95% CI 1.0-3.8), and 3.7 (95% CI 2.9-4.5), respectively. Median estimated population-attributable fraction for TB was as high as 0.4%. HCWs are at higher than average risk for TB. Sound TB infection control measures should be implemented in all health care facilities with patients suspected of having infectious TB.
Figures

References
-
- Menzies D, Joshi R, Pai M. Risk of tuberculosis infection and disease associated with work in health care settings. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2007;11:593–605. - PubMed
-
- Sepkowitz KA. Tuberculosis and the health care worker: a historical perspective. Ann Intern Med. 1994;120:71–9. - PubMed
-
- Jensen PA, Lambert LA, Iademarco MF, Ridzon R. Guidelines for preventing the transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in health care settings, 2005. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2005;54(RR-17):1–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
