Shikonin extracted from medicinal Chinese herbs exerts anti-inflammatory effect via proteasome inhibition
- PMID: 21392503
- PMCID: PMC3299007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.02.043
Shikonin extracted from medicinal Chinese herbs exerts anti-inflammatory effect via proteasome inhibition
Abstract
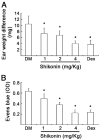
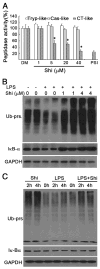
Shikonin, extracted from medicinal Chinese herb (Lithospermum erythrorhizo), was reported to exert anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer effects both in vitro and in vivo. We have found that proteasome was a molecular target of shikonin in tumor cells, but whether shikonin targets macrophage proteasome needs to be investigated. In the current study, we report that shikonin inhibited inflammation in mouse models as efficiently as dexamethasone. Shikonin at 4 μM reduced the Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-mediated TNFα release in rat primary macrophage cultures, and blocked the translocation of p65-NF-κB from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, associated with decreased proteasomal activity. Consistently, shikonin accumulated IκB-α, an inhibitor of NF-κB, and ubiquitinated proteins in rat primary macrophage cultures, demonstrating that the proteasome is a target of shikonin under inflammatory conditions. Shikonin also induced macrophage cell apoptosis and cell death. These results demonstrate for the first time that proteasome inhibition by shikonin contributes to its anti-inflammatory effect. The novel finding about macrophage proteasome as a target of shikonin suggests that this medicinal compound has great potential to be developed into an anti-inflammatory agent.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Shikonin Suppresses Lymphangiogenesis via NF-κB/HIF-1α Axis Inhibition.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(11):1659-1666. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b18-00329. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 30381665
-
Shikonin exerts antitumor activity via proteasome inhibition and cell death induction in vitro and in vivo.Int J Cancer. 2009 May 15;124(10):2450-9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24195. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19165859 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects in a murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Aug;16(4):475-80. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.04.020. Epub 2013 May 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23651796
-
[Antitumor effect research progress of shikonin and its derivatives].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012 May;47(5):588-93. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22812000 Review. Chinese.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Shikonin on Skin Diseases: A Review.Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(8):1871-1895. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X21500889. Am J Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 34961421 Review.
Cited by
-
Platinum-containing compound platinum pyrithione is stronger and safer than cisplatin in cancer therapy.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 15;116:22-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2016.06.019. Epub 2016 Jul 2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27381943 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine Regulating Lymphangiogenesis: A Literature Review.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 3;11:1259. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01259. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33013360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress in mechanism of anticancer action of shikonin targeting reactive oxygen species.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 11;15:1416781. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1416781. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39076592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α sensitizes breast cancer cells to natural products with proteasome-inhibitory activity leading to apoptosis.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 24;9(11):e113783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113783. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25419573 Free PMC article.
-
Shikonin inhibits CEBPD downregulation in IL‑17‑treated HaCaT cells and in an imiquimod‑induced psoriasis model.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Sep;22(3):2263-2272. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11315. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32705251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An B, Goldfarb RH, Siman R, Dou QP. Novel dipeptidyl proteasome inhibitors overcome Bcl-2 protective function and selectively accumulate the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 and induce apoptosis in transformed, but not normal, human fibroblasts. Cell Death Differ. 1998;5:1062–1075. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle PA, Henkel T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:141–179. - PubMed
-
- Biswas DK, Iglehart JD. Linkage between EGFR family receptors and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol. 2006;209:645–652. - PubMed
-
- Blackham A, Woods FAM. Immune complex mediated inflammation in the mouse peritoneal cavity. J Phamacol Meth. 1986;15:77–85. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ, Howard MZ. Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives. Phytother Res. 2002;16:199–209. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

