Angiotensin peptides and lung cancer
- PMID: 21395552
- PMCID: PMC3314267
- DOI: 10.2174/156800911795538048
Angiotensin peptides and lung cancer
Abstract
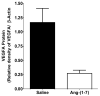
Lung cancer is a leading cause of death in both men and women, with over 1,000,000 new cases diagnosed worldwide annually and a 5-year survival rate of only 14%, a figure that has improved little in the past thirty years. This poor prognosis suggests a need for novel approaches for the treatment and prevention of lung cancer. The renin-angiotensin system is an established, primary regulator of blood pressure, homeostasis, and natriuresis; however, compelling evidence indicates that the angiotensin peptides also play a role in cell proliferation and inflammation. Angiotensin II is a vasoconstrictor, a mitogen, and an angiogenic factor, while angiotensin-(1-7) has vasodilator, anti-proliferative, and anti-angiogenic properties. This review focuses on studies examining the renin-angiotensin system in pulmonary cancers and whether clinical intervention of this pathway may serve as an effective chemotherapeutic and/or chemopreventive modality for lung cancer.
Figures

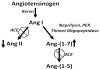

References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009;59:225–249. - PubMed
-
- Dowell JE. Small cell lung cancer: Are we making progress? Am. J. Med. Sci. 2010;339:68–76. - PubMed
-
- Cokkinides V, Bandi P, McMahon C, Jemal A, Glynn T, Ward E. Tobacco control in the united states--recent progress and opportunities. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2009;59:352–365. - PubMed
-
- Tallant EA, Menon J, Soto-Pantoja DR, Gallagher PE. Angiotensin peptides and cancer. In: Kastin AJ, editor. The Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides. Elsevier; 2006. Chapter 66.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

