Association of host genetic risk factors with the course of cytomegalovirus retinitis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus
- PMID: 21396623
- PMCID: PMC3103625
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2010.11.029
Association of host genetic risk factors with the course of cytomegalovirus retinitis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the effects of previously reported host genetics factors that influence cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis incidence, progression to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), and efficacy of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) for mortality, retinitis progression, and retinal detachment in patients with CMV retinitis and AIDS in the era of HAART.
Design: Prospective, multicenter, observational study.
Methods: Cox proportional hazards model based genetic association tests examined the influence of IL-10R1_S420L, CCR5-Δ32, CCR2-V64I, CCR5 promoter, and SDF-3'A polymorphisms among patients with mortality, retinitis progression, and retinal detachment. Participants were 203 European-American and 117 African-American patients with AIDS and CMV retinitis.
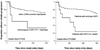
Results: European-American patients with the CCR5 +.P1.+ promoter haplotype showed increased risk for mortality (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.83; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.00-3.40; P = .05). Although the same haplotype also trended for increased risk for mortality in African-American patients, the result was not significant (HR = 2.28; 95% CI: 0.93-5.60; P = .07). However, this haplotype was associated with faster retinitis progression in African Americans (HR = 5.22; 95% CI: 1.54-17.71; P = .007). Increased risk of retinitis progression was also evident for African-American patients with the SDF1-3'A variant (HR = 3.89; 95% CI: 1.42-10.60; P = .008). In addition, the SDF1-3'A variant increased the retinal detachment risk in this patient group (HR = 3.05; 95% CI: 1.01-9.16; P = .05).
Conclusion: Besides overall immune health, host genetic factors influence mortality, retinitis progression, and retinal detachment in patients with AIDS and CMV retinitis that are receiving HAART.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have conflict of interest with any aspect of this study.
Figures
References
-
- Gallant JE, Moore RD, Richman DD, Keruly J, Chaisson RE. Incidence and natural history of cytomegalovirus disease in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus disease treated with zidovudine. The Zidovudine Epidemiology Study Group. J Infect Dis. 1992;166(6):1223–1227. - PubMed
-
- Hoover DR, Peng Y, Saah A, et al. Occurrence of cytomegalovirus retinitis after human immunodeficiency virus immunosuppression. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996;114(7):821–827. - PubMed
-
- Pertel P, Hirschtick R, Phair J, et al. Risk of developing cytomegalovirus retinitis in persons infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(11):1069–1074. - PubMed
-
- Studies of ocular complications of AIDS (LSOCA) Research Group ACTGA. Studies of ocular complications of AIDS Foscarnet-Ganciclovir Cytomegalovirus Retinitis Trial: 1. Rationale, design, and methods. Control Clin Trials. 1992;13(1):22–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ULI RR024996/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR 05096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 27660/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 27674/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR00865/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY008067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 27663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI32783/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY 08052/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY 08067/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR00043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI 27670/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR00096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CO012400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 EY 08057/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR 00350/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- Z99 CA999999/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 5M01 RR00046/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI25868/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical