Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1 is downregulated during expansion of antigen-specific CD8 T cells following primary and secondary Listeria monocytogenes infections
- PMID: 21396722
- PMCID: PMC3092857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2011.02.002
Vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1 is downregulated during expansion of antigen-specific CD8 T cells following primary and secondary Listeria monocytogenes infections
Abstract
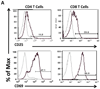
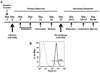
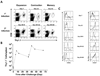
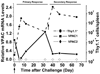
As regulation of CD8 T cell homeostasis is incompletely understood, we investigated the expression profile of the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptors, VPAC1 and VPAC2, on CD8 T cells throughout an in vivo immune response. Herein, we show that adoptively transferred CD8 T cells responding to a Listeria monocytogenes infection significantly downregulated, functionally active VPAC1 protein expression during primary and secondary expansion. VPAC1 mRNA expression was restored during contraction and regained naïve levels in primary, but remained low during secondary, memory generation. VIP co-administration with primary infection suppressed CD8 T cell expansion (≈ 50%). VPAC2 was not detected at any time points throughout primary and secondary infections. Collectively, our data demonstrate that functionally active VPAC1 is dynamically downregulated to render expanding CD8 T cells unresponsive to VIP.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bellinger DL, Lorton D, Brouxhon S, Felten S, Felten DL. The significance of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in immunomodulation. Adv Neuroimmunol. 1996;6:5–27. - PubMed
-
- Bellinger DL, Lorton D, Horn L, Brouxhon S, Felten SY, Felten DL. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) innervation of rat spleen, thymus, and lymph nodes. Peptides. 1997;18:1139–1149. - PubMed
-
- Bemelmans MH, Abramowicz D, Gouma DJ, Goldman M, Buurman WA. In vivo T cell activation by anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody induces soluble TNF receptor release in mice. Effects of pentoxifylline, methylprednisolone, anti-TNF, and anti-IFN-gamma antibodies. J Immunol. 1994;153:499–506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

