Anxiety states induced by post-weaning social isolation are mediated by CRF receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus
- PMID: 21396988
- PMCID: PMC3109218
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.03.003
Anxiety states induced by post-weaning social isolation are mediated by CRF receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus
Abstract
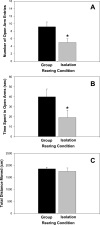
Post-weaning social isolation of rats is utilized as a model of early life stress. We have previously demonstrated that rats exposed to post-weaning social isolation exhibit greater anxiety-like behaviors as adults. Furthermore, these rats exhibit greater density of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) type 2 receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Therefore, we examined whether antagonism of CRF(2) receptors in the dorsal raphe nucleus reverses the effects of post-weaning social isolation on anxiety states. Male rats were reared in isolation or in groups from day of weaning (postnatal day [PND] 21) to mid-adolescence (PND42) and then allowed to develop to early adulthood housed in groups. At PND62, rats were either infused with vehicle, the CRF(1) receptor antagonist antalarmin (0.25-0.5 μg) or the CRF(2) receptor antagonist antisauvagine-30 (2 μg) into the dorsal raphe nucleus, 20 min prior to being introduced to the elevated plus maze. Isolation-reared rats showed reduced open arm behavior compared to group-reared rats, confirming the anxiogenic effects of post-weaning social isolation. Infusion of the CRF(2) receptor antagonist, but not the CRF(1) receptor antagonist, into the dorsal raphe nucleus of isolation-reared rats increased open arm behavior when compared to that of group-reared rats. Overall, the findings suggest that CRF(2) receptors within the dorsal raphe nucleus mediate anxiety-like states following post-weaning social isolation, and CRF(2) receptors may represent an important target for the treatment of anxiety disorders following early life stressors.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Amat J, Tamblyn JP, Paul ED, Bland ST, Amat P, Foster AC, Watkins LR, Maier SF. Microinjection of urocortin 2 into the dorsal raphé nucleus activates serotonergic neurons and increases extracellular serotonin in the basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience. 2004;129:509–519. - PubMed
-
- Andersen SL. Trajectories of brain development: point of vulnerability or window of opportunity? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2003;27:3–18. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa H. Interaction between isolation rearing and social development on exploratory behavior in male rats. Behav. Processes. 2005;70:223–234. - PubMed
-
- Arakawa H. Ontogenetic interaction between social relationships and defensive burying behavior in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 2007;90:751–759. - PubMed
-
- Bale TL, Contarino A, Smith GW, Chan R, Gold LH, Sawchenko PE, Koob GE, Vale WW, Lee KF. Mice deficient for corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor-2 display anxiety-like behaviour and are hypersensitive to stress. Nat. Genet. 2000;24:410–414. - PubMed

