Hedgehog signaling in skin cancers
- PMID: 21397013
- PMCID: PMC3122959
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.03.002
Hedgehog signaling in skin cancers
Abstract
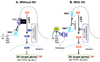
An increasing progress on the role of Hedgehog (Hh) signaling for carcinogenesis has been achieved since the link of Hh pathway to human cancer was firstly established. In particular, the critical role of Hh signaling in the development of Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) has been convincingly demonstrated by genetic mutation analyses, mouse models of BCCs, and successful clinical trials of BCCs using Hh signaling inhibitors. In addition, the Hh pathway activity is also reported to be involved in the pathogenesis of Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC), melanoma and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. These findings have significant new paradigm on Hh signaling transduction, its mechanisms in skin cancer and even therapeutic approaches for BCC. In this review, we will summarize the major advances in the understanding of Hh signaling transduction, the roles of Hh signaling in skin cancer development, and the current implications of "mechanism-based" therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: No potential conflict of interests to be disclosed
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in the treatment of Basal cell carcinoma: Hedgehog inhibitors.Semin Oncol. 2012 Apr;39(2):139-44. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2012.01.011. Semin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22484185 Review.
-
Loss of Primary Cilia Drives Switching from Hedgehog to Ras/MAPK Pathway in Resistant Basal Cell Carcinoma.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 Jul;139(7):1439-1448. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.11.035. Epub 2019 Jan 29. J Invest Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30707899 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic cross-talk of hedgehog and interleukin-6 signaling drives growth of basal cell carcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2018 Dec 1;143(11):2943-2954. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31724. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29987839 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical implications of hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitors.Chin J Cancer. 2011 Jan;30(1):13-26. doi: 10.5732/cjc.010.10540. Chin J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21192841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperative Hedgehog/GLI and JAK/STAT signaling drives immunosuppressive tryptophan/kynurenine metabolism via synergistic induction of IDO1 in skin cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Feb 17;23(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02101-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 39962447 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Gene expression profile identifies distinct molecular subtypes and potential therapeutic genes in Merkel cell carcinoma.Transl Oncol. 2020 Nov;13(11):100816. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100816. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32771971 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signaling pathways in the adrenal cortex: Links to stem/progenitor biology and neoplasia.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Apr 15;445:42-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27940298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin cancer biology and barriers to treatment: Recent applications of polymeric micro/nanostructures.J Adv Res. 2021 Jun 16;36:223-247. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.014. eCollection 2022 Feb. J Adv Res. 2021. PMID: 35127174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor Suppressor Function of CYLD in Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer.J Skin Cancer. 2011;2011:614097. doi: 10.1155/2011/614097. Epub 2011 Dec 17. J Skin Cancer. 2011. PMID: 22235375 Free PMC article.
-
Investigational Notch and Hedgehog inhibitors--therapies for cardiovascular disease.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011 Dec;20(12):1649-64. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2011.628658. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2011. PMID: 22007748 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nusslein-Volhard C, Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in drosophila. Nature. 1980;287(5785):795–801. - PubMed
-
- Roessler E, Belloni E, Gaudenz K, Jay P, Berta P, Scherer SW, Tsui LC, Muenke M. Mutations in the human Sonic Hedgehog gene cause holoprosencephaly. Nat Genet. 1996 Nov;14(3):357–360. - PubMed
-
- Belloni E, Muenke M, Roessler E, Traverso G, Siegel-Bartelt J, Frumkin A, Mitchell HF, Donis-Keller H, Helms C, Hing AV, Heng HH, Koop B, Martindale D, Rommens JM, Tsui LC, Scherer SW. Identification of Sonic hedgehog as a candidate gene responsible for holoprosencephaly. Nat Genet. 1996 Nov;14(3):353–356. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwenhuis E, Hui CC. Hedgehog signaling and congenital malformations. Clin. Genet. 67(2005):193–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

