Experience-dependent structural plasticity in the cortex
- PMID: 21397343
- PMCID: PMC3073830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.02.001
Experience-dependent structural plasticity in the cortex
Abstract
Synapses are the fundamental units of neuronal circuits. Synaptic plasticity can occur through changes in synaptic strength, as well as through the addition/removal of synapses. Two-photon microscopy in combination with fluorescence labeling offers a powerful tool to peek into the living brain and follow structural reorganization at individual synapses. Time-lapse imaging depicts a dynamic picture in which experience-dependent plasticity of synaptic structures varies between different cortical regions and layers, as well as between neuronal subtypes. Recent studies have demonstrated that the formation and elimination of synaptic structures happens rapidly in a subpopulation of cortical neurons during various sensorimotor learning experiences, and that stabilized synaptic structures are associated with long lasting memories for the task. Therefore, circuit plasticity, mediated by structural remodeling, provides an underlying mechanism for learning and memory.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
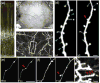
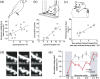
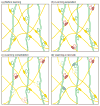
References
-
- James W. The Principles of Psychology. Vol. 1 Henry Holt & Co; 1890.
-
- Hubel DH, Wiesel TN. Early exploration of the visual cortex. Neuron. 1998;20:401–412. - PubMed
-
- Hubel DH, et al. Plasticity of ocular dominance columns in monkey striate cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977;278:377–409. - PubMed
-
- Wiesel TN, Hubel DH. Single-Cell Responses in Striate Cortex of Kittens Deprived of Vision in One Eye. J Neurophysiol. 1963;26:1003–1017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

