Identification of a therapeutic strategy targeting amplified FGF19 in liver cancer by Oncogenomic screening
- PMID: 21397858
- PMCID: PMC3061399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.040
Identification of a therapeutic strategy targeting amplified FGF19 in liver cancer by Oncogenomic screening
Abstract
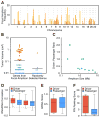
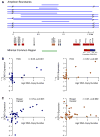
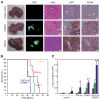
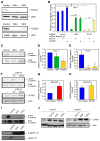
We screened 124 genes that are amplified in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using a mouse hepatoblast model and identified 18 tumor-promoting genes, including CCND1 and its neighbor on 11q13.3, FGF19. Although it is widely assumed that CCND1 is the main driving oncogene of this common amplicon (15% frequency in HCC), both forward-transformation assays and RNAi-mediated inhibition in human HCC cells established that FGF19 is an equally important driver gene in HCC. Furthermore, clonal growth and tumorigenicity of HCC cells harboring the 11q13.3 amplicon were selectively inhibited by RNAi-mediated knockdown of CCND1 or FGF19, as well as by an anti-FGF19 antibody. These results show that 11q13.3 amplification could be an effective biomarker for patients most likely to respond to anti-FGF19 therapy.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Albertson DG, Collins C, McCormick F, Gray JW. Chromosome aberrations in solid tumors. Nat Genet. 2003;34:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Azechi H, Nishida N, Fukuda Y, Nishimura T, Minata M, Katsuma H, Kuno M, Ito T, Komeda T, Kita R, et al. Disruption of the p16/cyclin D1/retinoblastoma protein pathway in the majority of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncology. 2001;60:346–354. - PubMed
-
- Briata P, Ilengo C, Corte G, Moroni C, Rosenfeld MG, Chen CY, Gherzi R. The Wnt/beta-catenin-->Pitx2 pathway controls the turnover of Pitx2 and other unstable mRNAs. Mol Cell. 2003;12:1201–1211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

