Deletion of the p85alpha regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in cone photoreceptor cells results in cone photoreceptor degeneration
- PMID: 21398281
- PMCID: PMC3109053
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.10-7139
Deletion of the p85alpha regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase in cone photoreceptor cells results in cone photoreceptor degeneration
Abstract
Purpose: Downregulation of the retinal insulin/mTOR pathway in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa is linked to cone cell death, which can be delayed by systemic administration of insulin. A classic survival kinase linking extracellular trophic/growth factors with intracellular antiapoptotic pathways is phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), which the authors have shown to protect rod photoreceptors from stress-induced cell death. The role of PI3K in cones was studied by conditional deletion of its p85α regulatory subunit.
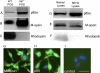
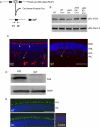
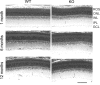
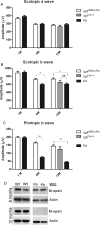
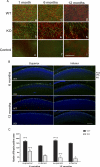
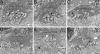
Methods: Mice expressing Cre recombinase in cones were bred to mice with a floxed pi3k gene encoding the p85α regulatory subunit of the PI3K and were back-crossed to ultimately generate offspring with cone-specific p85α knockout (cKO). Cre expression and cone-specific localization were confirmed by Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry (IHC), respectively. Cone structural integrity was determined by IHC using peanut agglutinin and an M-opsin-specific antibody. Electroretinography (ERG) was used to assess rod and cone photoreceptor function. Retinal structure was examined by light and electron microscopy.
Results: An age-related cone degeneration was found in cKO mice, evidenced by a reduction in photopic ERG amplitudes and loss of cone cells. By 12 months of age, approximately 78% of cones had died, and progressive disorganization of synaptic ultrastructure was noted in surviving cone terminals in cKO retinas. Rod viability was unaffected in p85α cKO mice.
Conclusions: The present study suggests that PI3K signaling pathway is essential for cone survival in the mouse retina.
Figures
References
-
- Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296:1655–1657 - PubMed
-
- Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, et al. Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science. 1997;275:661–665 - PubMed
-
- Fukami K, Endo T, Imamura M, Takenawa T. alpha-Actinin and vinculin are PIP2-binding proteins involved in signaling by tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:1518–1522 - PubMed
-
- Fukami K, Sawada N, Endo T, Takenawa T. Identification of a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate-binding site in chicken skeletal muscle alpha-actinin. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:2646–2650 - PubMed
-
- Guo X, Ghalayini AJ, Chen H, Anderson RE. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in bovine photoreceptor rod outer segments. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1997;38:1873–1882 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

