siRNA-induced liver ApoB knockdown lowers serum LDL-cholesterol in a mouse model with human-like serum lipids
- PMID: 21398511
- PMCID: PMC3090230
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M012872
siRNA-induced liver ApoB knockdown lowers serum LDL-cholesterol in a mouse model with human-like serum lipids
Abstract
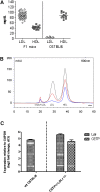
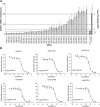
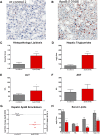
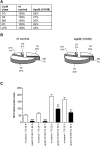
Increased serum apolipoprotein (apo)B and associated LDL levels are well-correlated with an increased risk of coronary disease. ApoE⁻/⁻ and low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLr)⁻/⁻ mice have been extensively used for studies of coronary atherosclerosis. These animals show atherosclerotic lesions similar to those in humans, but their serum lipids are low in apoB-containing LDL particles. We describe the development of a new mouse model with a human-like lipid profile. Ldlr CETP⁺/⁻ hemizygous mice carry a single copy of the human CETP transgene and a single copy of a LDL receptor mutation. To evaluate the apoB pathways in this mouse model, we used novel short-interfering RNAs (siRNA) formulated in lipid nanoparticles (LNP). ApoB siRNAs induced up to 95% reduction of liver ApoB mRNA and serum apoB protein, and a significant lowering of serum LDL in Ldlr CETP⁺/⁻ mice. ApoB targeting is specific and dose-dependent, and it shows lipid-lowering effects for over three weeks. Although specific triglycerides (TG) were affected by ApoB mRNA knockdown (KD) and the total plasma lipid levels were decreased by 70%, the overall lipid distribution did not change. Results presented here demonstrate a new mouse model for investigating additional targets within the ApoB pathways using the siRNA modality.
Figures




References
-
- Wouters K., Shiri-Sverdlov R., van Gorp P. J., van Bilsen M., Hofker M. H. 2005. Understanding hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis: lessons from genetically modified apoe and ldlr mice. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 43: 470–479. - PubMed
-
- Maron D. J., Fazio S., Linton M. F. 2000. Current perspectives on statins. Circulation. 101: 207–213. - PubMed
-
- Hobbs H. H., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. 1992. Molecular genetics of the LDL receptor gene in familial hypercholesterolemia. Hum. Mutat. 1: 445–466. - PubMed
-
- Havekes L., de Wit E., Leuven J. G., Klasen E., Utermann G., Weber W., Beisiegel U. 1986. Apolipoprotein E3-Leiden. A new variant of human apolipoprotein E associated with familial type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Hum. Genet. 73: 157–163. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

