Mechanistic control of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM1) splice isoforms by the heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear proteins hnRNP L, hnRNP A1, and hnRNP M
- PMID: 21398516
- PMCID: PMC3091213
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.204057
Mechanistic control of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM1) splice isoforms by the heterogeneous nuclear ribonuclear proteins hnRNP L, hnRNP A1, and hnRNP M
Abstract
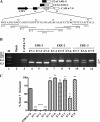
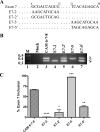
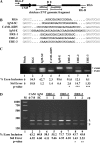
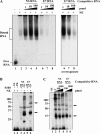
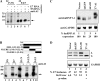
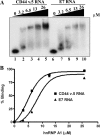
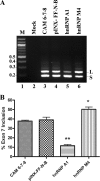
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule-1 (CEACAM1) is expressed in a variety of cell types and is implicated in carcinogenesis. Alternative splicing of CEACAM1 pre-mRNA generates two cytoplasmic domain splice variants characterized by the inclusion (L-isoform) or exclusion (S-isoform) of exon 7. Here we show that the alternative splicing of CEACAM1 pre-mRNA is regulated by novel cis elements residing in exon 7. We report the presence of three exon regulatory elements that lead to the inclusion or exclusion of exon 7 CEACAM1 mRNA in ZR75 breast cancer cells. Heterologous splicing reporter assays demonstrated that the maintenance of authentic alternative splicing mechanisms were independent of the CEACAM1 intron sequence context. We show that forced expression of these exon regulatory elements could alter CEACAM1 splicing in HEK-293 cells. Using RNA affinity chromatography, three members of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein family (hnRNP L, hnRNP A1, and hnRNP M) were identified. RNA immunoprecipitation of hnRNP L and hnRNP A1 revealed a binding motif located central and 3' to exon 7, respectively. Depletion of hnRNP A1 or L by RNAi in HEK-293 cells promoted exon 7 inclusion, whereas overexpression led to exclusion of the variable exon. By contrast, overexpression of hnRNP M showed exon 7 inclusion and production of CEACAM1-L mRNA. Finally, stress-induced cytoplasmic accumulation of hnRNP A1 in MDA-MB-468 cells dynamically alters the CEACAM1-S:CEACAM1:L ratio in favor of the l-isoform. Thus, we have elucidated the molecular factors that control the mechanism of splice-site recognition in the alternative splicing regulation of CEACAM1.
Figures



References
-
- Nittka S., Günther J., Ebisch C., Erbersdobler A., Neumaier M. (2004) Oncogene 23, 9306–9313 - PubMed
-
- Hsieh J. T., Luo W., Song W., Wang Y., Kleinerman D. I., Van N. T., Lin S. H. (1995) Cancer Res. 55, 190–197 - PubMed
-
- Riethdorf L., Lisboa B. W., Henkel U., Naumann M., Wagener C., Löning T. (1997) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 45, 957–963 - PubMed
-
- Gray-Owen S. D., Blumberg R. S. (2006) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 433–446 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

