Regulation of hepatic fat and glucose oxidation in rats with lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance
- PMID: 21400553
- PMCID: PMC3077048
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.24170
Regulation of hepatic fat and glucose oxidation in rats with lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance
Abstract
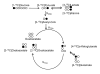
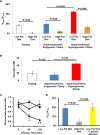
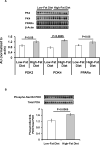
Pyruvate dehydrogenase plays a critical role in the regulation of hepatic glucose and fatty acid oxidation; however, surprisingly little is known about its regulation in vivo. In this study we examined the individual effects of insulin and substrate availability on the regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux (V(PDH) ) to tricarboxylic acid flux (V(TCA) ) in livers of awake rats with lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance. V(PDH) /V(TCA) flux was estimated from the [4-(13) C]glutamate/[3-(13) C]alanine enrichments in liver extracts and assessed under conditions of fasting and during a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp, whereas the effects of increased plasma glucose concentration on V(PDH) /V(TCA) flux was assessed during a hyperglycemic clamp in conjunction with infusions of somatostatin and insulin to maintain basal concentrations of insulin. The effects of increases in both glucose and insulin on V(PDH) /V(TCA) were examined during a hyperinsulinemic-hyperglycemic clamp. The effects of chronic lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance on this flux were also examined by performing these measurements in rats fed a high-fat diet for 3 weeks. Using this approach we found that fasting V(PDH) /V(TCA) was reduced by 95% in rats with hepatic insulin resistance (from 17.2 ± 1.5% to 1.3 ± 0.7%, P < 0.00001). Surprisingly, neither hyperinsulinemia per se or hyperglycemia per se were sufficient to increase V(PDH) /V(TCA) flux. Only under conditions of combined hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia did V(PDH) /V(TCA) flux increase (44.6 ± 3.2%, P < 0.0001 versus basal) in low-fat fed animals but not in rats with chronic lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance.
Conclusion: These studies demonstrate that the combination of both hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia are required to increase V(PDH) /V(TCA) flux in vivo and that this flux is severely diminished in rats with chronic lipid-induced hepatic insulin resistance.
2011 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Holness MJ, Sugden MC. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity by reversible phosphorylation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:1143–1151. - PubMed
-
- Strumilo S. Short-term regulation of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. Acta Biochim Pol. 2005;52:759–764. - PubMed
-
- Randle PJ, Garland PB, Hales CN, Newsholme EA. The glucose fatty-acid cycle. Its role in insulin sensitivity and the metabolic disturbances of diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1963;1:785–789. - PubMed
-
- Rennie SM, Park BS, Zammit VA. A switch in the direction of the effect of insulin on the partitioning of hepatic fatty acids for the formation of secreted triacylglycerol occurs in vivo, as predicted from studies with perfused livers. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267:935–941. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
