Interactions of glutathione transferases with 4-hydroxynonenal
- PMID: 21401344
- PMCID: PMC4464844
- DOI: 10.3109/03602532.2011.558092
Interactions of glutathione transferases with 4-hydroxynonenal
Abstract
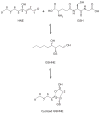
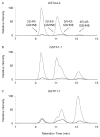
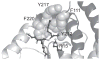
Electrophilic products of lipid peroxidation are important contributors to the progression of several pathological states. The prototypical α,β-unsaturated aldehyde, 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), triggers cellular events associated with oxidative stress, which can be curtailed by the glutathione-dependent elimination of HNE. The glutathione transferases (GSTs) are a major determinate of the intracellular concentration of HNE and can influence susceptibility to toxic effects, particularly when HNE and GST levels are altered in disease states. In this article, we provide a brief summary of the cellular effects of HNE, followed by a review of its GST-catalyzed detoxification, with an emphasis on the structural attributes that play an important role in the interactions with alpha-class GSTs. Some of the key determining characteristics that impart high alkenal activity reside in the unique C-terminal interactions of the GSTA4-4 enzyme. Studies encompassing both kinetic and structural analyses of related isoforms will be highlighted, with additional attention to stereochemical aspects that demonstrate the capacity of GSTA4-4 to detoxify both enantiomers of the biologically relevant racemic mixture while generating a select set of diastereomeric products with subsequent implications. A summary of the literature that examines the interplay between GSTs and HNE in model systems relevant to oxidative stress will also be discussed to demonstrate the magnitude of importance of GSTs in the overall detoxification scheme.
Figures
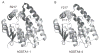

References
-
- Adman ET, Le Trong I, Stenkamp RE, Nieslanik BS, Dietze EC, Tai G, et al. Localization of the C-terminus of rat glutathione S-transferase A1-1: crystal structure of mutants W21F and W21F/F220Y. Proteins. 2001;42:192–200. - PubMed
-
- Alary J, Debrauwer L, Fernandez Y, Cravedi JP, Rao D, Bories G. 1,4-dihydroxynonene mercapturic acid, the major end metabolite of exogenous 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal, is a physiological component of rat and human urine. Chem Res Toxicol. 1998;11:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Alary J, Gueraud F, Cravedi JP. Fate of 4-hydroxynonenal in vivo: disposition and metabolic pathways. Mol Aspects Med. 2003;24:177–187. - PubMed
-
- Aldini G, Gamberoni L, Orioli M, Beretta G, Regazzoni L, Maffei Facino R, et al. Mass spectrometric characterization of covalent modification of human serum albumin by 4-hydroxy-trans- 2-nonenal. J Mass Spectrom. 2006;41:1149–1161. - PubMed
-
- Alin P, Danielson UH, Mannervik B. 4-hydroxyalk-2-enals are substrates for glutathione transferase. FEBS Lett. 1985;179:267–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
