Therapeutic modulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 21401517
- PMCID: PMC3893117
- DOI: 10.2174/138920111798281171
Therapeutic modulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
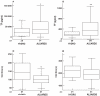
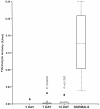
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute lung injury (ALI) are characterized by excessive intraalveolar fibrin deposition, driven, at least in part by inflammation. The imbalance between activation of coagulation and inhibition of fibrinolysis in patients with ALI/ARDS favors fibrin formation and appears to occur both systemically and in the lung and airspace. Tissue factor (TF), a key mediator of the activation of coagulation in the lung, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. As such, there have been numerous investigations modulating TF activity in a variety of experimental systems in order to develop new therapeutic strategies for ALI/ARDS. This review will summarize current understanding of the role of TF and other proteins of the coagulation cascade as well the fibrinolysis pathway in the development of ALI/ARDS with an emphasis on the pathways that are potential therapeutic targets. These include the TF inhibitor pathway, the protein C pathway, antithrombin, heparin, and modulation of fibrinolysis through plasminogen activator- 1 (PAI-1) or plasminogen activators (PA). Although experimental studies show promising results, clinical trials to date have proven unsuccessful in improving patient outcomes. Modulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis has complex effects on both hemostasis and inflammatory pathways and further studies are needed to develop new treatment strategies for patients with ALI/ARDS.
Figures

References
-
- Hofstra JJ, Juffermans NP, Schultz MJ, Zweers MM. Pulmonary coagulopathy as a new target in lung injury--a review of available pre-clinical models. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008;15:588–595. - PubMed
-
- Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The acute respiratory distress syndrome network. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;342:1301–1308. - PubMed
-
- dos Santos CC, Slutsky AS. Mechanotransduction, ventilator-induced lung injury and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2000;26:638–642. - PubMed
-
- Ware LB, Bastarache JA, Wang L. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in human acute lung injury--new therapeutic targets? Keio J. Med. 2005;54:142–149. - PubMed
-
- Herridge MS, Cheung AM, Tansey CM, Matte-Martyn A, Diaz-Granados N, Al-Saidi F, Cooper AB, Guest CB, Mazer CD, Mehta S, Stewart TE, Barr A, Cook D, Slutsky AS. One-year outcomes in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:683–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

