Anti-tumour and anti-angiogenetic effects of zoledronic acid on human non-small-cell lung cancer cell line
- PMID: 21401755
- PMCID: PMC6496192
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2011.00745.x
Anti-tumour and anti-angiogenetic effects of zoledronic acid on human non-small-cell lung cancer cell line
Abstract
Objectives: Although emerging data suggest that zoledronic acid (Zol) may have different anti-tumour activities against a broad range of cancers, its effects on lung cancer remain largely unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate in vitro the anti-tumoural and anti-angiogenetic effect of zoledronic acid in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells.
Material and methods: We treated A549 NSCLC cells with zoledronic acid to investigate survival, cell cycle activity, anti-angiogenic activity and apoptotic responses to it.
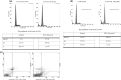
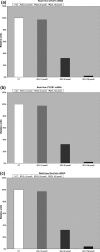
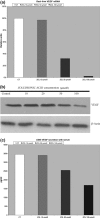
Results: We observed that highest Zol concentration (100μm) caused arrest in G1 phase of the cell cycle and also induced different percentages of apoptosis in presence (0.9% versus 4.4%) or absence (2.4% versus 28.5%) of serum (P=0.0001). Zol concentration from 5 to 100μm for 2 days induced significant concentration-dependent cell death in adherent cells. Furthermore, Zol (10-100μm) induced dose-dependent reduction both of mRNA and protein expression of VEGF associated with parallel decrease in VEGF secretion in the culture medium.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results support a possible anti-cancer and anti-angiogenetic activity of Zol. Our data may not only provide a basis for the clinical use of this drug as preventive agent of bone metastases but also suggest that Zol deserves attention as an anti-cancer agent in non-small-cell lung cancer.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Yuasa T, Kimura S, Ashihara E, Habuchi T, Maekawa T (2007) Zoledronic acid – a multiplicity of anti‐cancer action. Curr. Med. Chem. 14, 2126–2135. - PubMed
-
- Wood J, Bonjean K, Ruetz S, Bellahcène A, Devy L, Foidart JM et al. (2002) Novel antiangiogenic effects of the bisphosphonate compound zoledronic acid. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302, 1055–1061. - PubMed
-
- Santini D, Vincenzi B, Avvisati G, Dicuonzo G, Battistoni F, Gavasci M et al. (2002) Pamidronate induces modifications of circulating angiogenetic factors in cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 8, 1080–1084. - PubMed
-
- Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M, Cobleigh M, Perez EA et al. (2007) Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N. Eng. J. Med. 357, 2666–2676. - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam SS et al. (2008) Outcomes for elderly, advanced‐stage non‐small‐cell lung cancer patients treated with bevacizumab in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel: analysis of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial 4599. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

