Influence of proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, on early development of fertilized mouse eggs, via inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt
- PMID: 21401757
- PMCID: PMC6495843
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.2011.00743.x
Influence of proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase, on early development of fertilized mouse eggs, via inhibition of phosphorylation of Akt
Abstract
Objectives: Proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (PIPP) is one of the signal-modifying enzymes that play pivotal regulatory roles in PI3K signalling pathway. The aim of this study was to determine the role of PIPP in early development of fertilized mouse eggs, via inhibition of Akt activity and subsequent downstream signalling events.
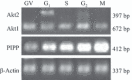
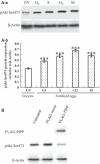
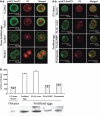
Materials and methods: The mRNA transcript levels of endogenous PIPP and Akt1, Akt2, Akt3 were detected in G(1) , S, G(2) and M phases of fertilized mouse eggs by RT-PCR. Levels of exogenous PIPP, phosphorylated Akt at Ser473, dephosphorylated cdc2 at Tyr15 and levels of CCNB1, were detected respectively by immunoblotting. Changes in Akt localization were observed by fluoroimmunoassay; meanwhile, changes in activity of Akt and its downstream MPF were detected. Percentages of cells undergoing division were determined by counting, using a dissecting microscope.
Results: PIPP and Akt1 transcripts were detectable in G(1), S, G(2) and M phases of fertilized mouse eggs, but Akt2 and Akt3 were not. We also observed that overexpression of PIPP in fertilized eggs decreased expression of phosphorylated Akt at Ser473 and altered membrane localization of phosphorylated Akt at Ser473 specifically. Furthermore, overexpression of PIPP resulted in decreases in mitosis-phase promoting factor activity, level of dephosphorylated cdc2 at Tyr15 and cleavage rate of fertilized mouse eggs.
Conclusions: Our data suggest, for the first time, that PIPP may affect development of fertilized mouse eggs by inhibition of level of phosphorylated Akt at Ser473 and subsequent inhibition of downstream signal cascades.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hormesis of low-dose inhibition of pAkt1 (Ser473) followed by a great increase of proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase (PIPP) level in oocytes.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2021 Mar;57(3):342-349. doi: 10.1007/s11626-021-00546-w. Epub 2021 Feb 3. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2021. PMID: 33537929
-
F-actin rearrangement is regulated by mTORC2/Akt/Girdin in mouse fertilized eggs.Cell Prolif. 2016 Dec;49(6):740-750. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12285. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Cell Prolif. 2016. PMID: 27666957 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of protein kinase B/AKT in early development of mouse fertilized eggs.Biol Reprod. 2007 Sep;77(3):560-8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.060269. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Biol Reprod. 2007. PMID: 17554083
-
PTEN and Other PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 Lipid Phosphatases in Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 2;21(23):9189. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239189. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33276499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of PtdIns(3,4,5)P3/Akt signalling by inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2016 Feb;44(1):240-52. doi: 10.1042/BST20150214. Biochem Soc Trans. 2016. PMID: 26862211 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement of CaMKII in regulating the release of diplotene-arrested mouse oocytes by pAkt1 (Ser473).Cell Cycle. 2019 Nov;18(21):2986-2997. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1666596. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31530151 Free PMC article.
-
Gel-based and gel-free identification of proteins and phosphopeptides during egg-to-larva transition in polychaete Neanthes arenaceodentata.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e38814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038814. Epub 2012 Jun 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719953 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitchell CA, Gurung R, Kong AM, Dyson JM, Tan A, Ooms LM (2002) Inositol polyphosphate 5‐phosphatases: lipid phosphatases with flair. IUBMB Life 53, 25–36. - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki Y, Takenawa T (1999) Novel inositol polyphosphate 5‐phosphatase localizes at membrane ruffles. J. Biol. Chem. 17, 36790–36795. - PubMed
-
- Brazil DP, Hemmings BA (2001) Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26, 657–664. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

