Critical and off-critical miscibility transitions in model extracellular and cytoplasmic myelin lipid monolayers
- PMID: 21402031
- PMCID: PMC3059582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.02.009
Critical and off-critical miscibility transitions in model extracellular and cytoplasmic myelin lipid monolayers
Abstract
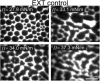
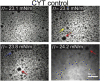
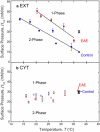
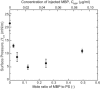
Monolayers based on the composition of the cytoplasmic (CYT) or extracellular (EXT) sides of the myelin bilayer form coexisting immiscible liquid phases similar to the liquid-ordered/liquid-disordered phases in phospholipid/cholesterol monolayers. Increasing the temperature or surface pressure causes the two liquid phases to mix, although in significantly different fashion for the CYT and EXT monolayers. The cerebroside-rich EXT monolayer is near a critical composition and the domains undergo coalescence and a circle-to-stripe transition along with significant roughening of the domain boundaries before mixing. The phase transition in the cerebroside-free cytoplasmic side occurs abruptly without domain coalescence; hence, the cytoplasmic monolayer is not near a critical composition, although the domains exhibit shape instabilities within 1-2 mN/m of the transition. The change in mixing pressure decreases significantly with temperature for the EXT monolayer, with dΠ(crit)/dT ∼ 1.5 mN/m/°C, but the mixing pressure of the CYT monolayer varies little with temperature. This is due to the differences in the nonideality of cholesterol interactions with cerebrosides (EXT) relative to phospholipids (CYT). EXT monolayers based on the composition of white matter from marmosets with experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis, remain phase-separated at higher surface pressures than control, while EAE CYT monolayers are similar to control. Myelin basic protein, when added to the CYT monolayer, increases lipid miscibility in CYT monolayers; likely done by altering the dipole density difference between the two phases.
Copyright © 2011 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relating domain size distribution to line tension and molecular dipole density in model cytoplasmic myelin lipid monolayers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9425-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106368108. Epub 2011 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21606329 Free PMC article.
-
Miscibility of ternary mixtures of phospholipids and cholesterol in monolayers, and application to bilayer systems.Biophys J. 2005 Jan;88(1):269-76. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.048439. Epub 2004 Oct 8. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15475588 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lipid interactions in autoimmune demyelination.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Jan 20;1688(1):10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2003.10.001. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 14732476
-
The self-organization of lipids and proteins of myelin at the membrane interface. Molecular factors underlying the microheterogeneity of domain segregation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jul-Aug;1778(7-8):1665-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.02.007. Epub 2008 Feb 21. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18342620 Review.
-
Mixing behavior of binary insoluble phospholipid monolayers. Analysis of the mixing properties of binary lecithin and cephalin systems by application of several surface and spreading techniques.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1990 Feb;31(1-2):1-110. doi: 10.1016/0001-8686(90)80003-i. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1990. PMID: 2178635 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Line Tension Measurement Methods for Lipid Monolayers at Liquid-Liquid Coexistence.Langmuir. 2019 Dec 3;35(48):16053-16061. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b01696. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Langmuir. 2019. PMID: 31343892 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous evolution of equilibrium morphology in phospholipid-cholesterol monolayers.Sci Adv. 2022 Apr 8;8(14):eabl9152. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl9152. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35385307 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Association Landscape of Myelin Basic Protein Portrays Formation of the Myelin Major Dense Line.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 10;7(1):4974. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05364-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28694532 Free PMC article.
-
Relating domain size distribution to line tension and molecular dipole density in model cytoplasmic myelin lipid monolayers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9425-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106368108. Epub 2011 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21606329 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion and hemifusion of cytoplasmic myelin lipid membranes are highly dependent on the lipid composition.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Mar;1818(3):402-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2011.10.015. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22047743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boggs J.M., Moscarello M.A. Structural organization of the human myelin membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1978;515:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Palaniyar N., Semotok J.L., Harauz G. Human proteolipid protein (PLP) mediates winding and adhesion of phospholipid membranes but prevents their fusion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1415:85–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

