Stress-dependent impairment of passive-avoidance memory by propranolol or naloxone
- PMID: 21402095
- PMCID: PMC3902981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.03.005
Stress-dependent impairment of passive-avoidance memory by propranolol or naloxone
Abstract
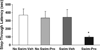
Previous work has shown that the effect of opioid-receptor blockade on memory modulation is critically dependent upon the intensity of stress. The current study determined the effect of adrenergic-receptor blockade on memory modulation under varied levels of stress and then compared the effect of adrenergic-receptor blockade under intense stress to that of a) opioid-receptor blockade and b) concurrent opioid- and adrenergic-receptor blockade. In the first experiment, the β-adrenergic-receptor blocker propranolol impaired retention in the passive-avoidance procedure when administered immediately after exposure to intense stress (passive-avoidance training followed by swim stress) but not mild stress (passive-avoidance training alone). In the second experiment, while separate administration of either propranolol or the opioid-receptor blocker naloxone immediately after exposure to intense stress impaired retention, the combined administration of propranolol and naloxone failed to do so. These findings demonstrate that the effect of β-adrenergic-receptor blockade or opioid-receptor blockade on memory modulation in the passive-avoidance procedure is dependent upon the intensity of stress, and suggest that concurrent inactivation of endogenous adrenergic- and opioid-based memory modulation systems under stressful conditions is protective of memory.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stress-dependent opioid and adrenergic modulation of newly retrieved fear memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Mar;109:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.11.013. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24291724 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade by propranolol enhances retention in a multitrial passive-avoidance procedure.Behav Neurosci. 2000 Dec;114(6):1256-60. Behav Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 11142659
-
Stress-dependent enhancement and impairment of retention by naloxone: evidence for an endogenous opioid-based modulatory system protective of memory.Behav Brain Res. 2009 Dec 14;205(1):290-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2009.06.007. Epub 2009 Jun 10. Behav Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19523491 Free PMC article.
-
The action of orexin B on passive avoidance learning. Involvement of neurotransmitters.Behav Brain Res. 2014 Oct 1;272:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.06.016. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24931796
-
Concurrent muscarinic and beta-adrenergic blockade in rats impairs place-learning in a water maze and retention of inhibitory avoidance.Brain Res. 1990 Apr 9;513(1):81-5. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91091-t. Brain Res. 1990. PMID: 2161697
Cited by
-
Immediate post-defeat infusions of the noradrenergic receptor antagonist propranolol impair the consolidation of conditioned defeat in male Syrian hamsters.Physiol Behav. 2015 Dec 1;152(Pt A):56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Physiol Behav. 2015. PMID: 26367452 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-dependent opioid and adrenergic modulation of newly retrieved fear memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Mar;109:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.11.013. Epub 2013 Nov 27. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24291724 Free PMC article.
-
The neuroenergetics of stress hormones in the hippocampus and implications for memory.Front Neurosci. 2015 May 6;9:164. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00164. eCollection 2015. Front Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25999811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Memory Impairing Effect of Propranolol on Consolidation and Reconsolidation for Various Learning Tasks.Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2023 Aug 3;60(3):271-282. doi: 10.29399/npa.28203. eCollection 2023. Noro Psikiyatr Ars. 2023. PMID: 37645086 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albucher RC, Liberzon I. Psychopharmacological treatment in PTSD: a critical review. J Psychiatr Res. 2002;36:355–367. - PubMed
-
- Beatty WW, Rush JR. Spatial working memory in rats: effects of monoaminergic antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1983;18:7–12. - PubMed
-
- Cahill L, Pham CA, Setlow B. Impaired memory consolidation in rats produced with beta-adrenergic blockade. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2000;74:259–266. - PubMed
-
- Christianson JP, Townson DH, Drugan RC. Comparison of intermittent shock and intermittent cold water swim stress on corticosterone and TNF-alpha at two time points after a forced swim test. Soc Neurosci Abs. 2003;756.5

