A randomized, controlled trial of raltegravir intensification in antiretroviral-treated, HIV-infected patients with a suboptimal CD4+ T cell response
- PMID: 21402547
- PMCID: PMC3068029
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiq138
A randomized, controlled trial of raltegravir intensification in antiretroviral-treated, HIV-infected patients with a suboptimal CD4+ T cell response
Abstract
Background: Some human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals are not able to achieve a normal CD4(+) T cell count despite prolonged, treatment-mediated viral suppression. We conducted an intensification study to assess whether residual viral replication contributes to replenishment of the latent reservoir and whether mucosal HIV-specific T cell responses limit the reservoir size.
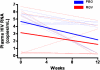
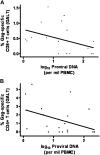
Methods: Thirty treated subjects with CD4(+) T cell counts of <350 cells/mm(3) despite viral suppression for ≥ 1 year were randomized to add raltegravir (400 mg twice daily) or matching placebo for 24 weeks. The primary end points were the proportion of subjects with undetectable plasma viremia (determined using an ultrasensitive assay with a lower limit of detection of <.3 copy/mL) and a change in the percentage of CD38(+)HLA-DR(+)CD8(+) T cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).
Results: The proportion of subjects with undetectable plasma viremia did not differ between the 2 groups (P = .42). Raltegravir intensification did not have a significant effect on immune activation or HIV-specific responses in PBMCs or gut-associated lymphoid tissue.
Conclusions: Low-level viremia is not likely to be a significant cause of suboptimal CD4(+) T cell gains during HIV treatment.
Clinical trials registration: NCT00631449.
Figures




Comment in
-
Hide and seek... Can we eradicate HIV by treatment intensification?J Infect Dis. 2011 Apr 1;203(7):894-7. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq150. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21402541 No abstract available.
References
-
- Palella FJ, Jr, Delaney KM, Moorman AC, et al. Declining morbidity and mortality among patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection. HIV Outpatient Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:853–60. - PubMed
-
- Moore DM, Hogg RS, Chan K, Tyndall M, Yip B, Montaner JS. Disease progression in patients with virological suppression in response to HAART is associated with the degree of immunological response. AIDS. 2006;20:371–7. - PubMed
-
- El-Sadr WM, Lundgren JD, Neaton JD, et al. CD4+ count-guided interruption of antiretroviral treatment. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2283–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- C06 RR - 12088/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K24AI069994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI087145/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1-RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI057020/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI055273/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH62246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI052745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- RR16482/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K23AI075985/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DPI OD00329/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI067854/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

