Trypanocidal furamidine analogues: influence of pyridine nitrogens on trypanocidal activity, transport kinetics, and resistance patterns
- PMID: 21402852
- PMCID: PMC3088251
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01551-10
Trypanocidal furamidine analogues: influence of pyridine nitrogens on trypanocidal activity, transport kinetics, and resistance patterns
Abstract
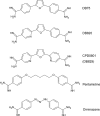
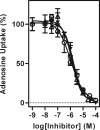
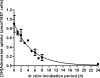
Current therapies for human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) are unsatisfactory and under threat from emerging drug resistance linked to the loss of transporters, e.g., the P2 aminopurine transporter (TbAT1). Here we compare the uptake and trypanocidal properties of furamidine (DB75), recently evaluated in clinical trials against stage 1 (haemolymphatic) HAT, and two aza analogues, DB820 and CPD0801 (DB829), which are candidate compounds for treatment of stage 2 (neurological) disease. Values of 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) determined in vitro against both wild-type and transporter mutant parasites were submicromolar, with DB75 trypanotoxicity shown to be better than and DB820 trypanotoxicity similar to that of the widely used veterinary trypanocide diminazene, while CPD0801 was less active. Activity correlated with uptake and with the minimum drug exposure time necessary to kill trypanosomes: DB75 accumulated at double and 10-fold the rates of DB820 and CPD0801, respectively. All three compounds inhibited P2-mediated adenosine transport with similar Ki values, indicating affinity values for this permease in the low to submicromolar range. Uptake of DB75, DB820, and CPD0801 was significantly reduced in tbat1-/- parasites and was sensitive to inhibition by adenine, showing that all three compounds are substrates for the P2 transporter. Uptake in vitro was significantly less than that seen with parasites freshly isolated from infected rats, correlating with a downregulation of P2 activity in vitro. We conclude that DB75, DB820, and CPD0801 are actively accumulated by Trypanosoma brucei brucei, with P2 as the main transport route. The aza analogues of DB75 accumulate more slowly than furamidine itself and reveal less trypanocidal activity in standard in vitro drug sensitivity assays.
Figures

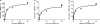
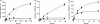
References
-
- Al-Salabi M. I., et al. 2007. Molecular interactions underlying the unusually high affinity of a novel Trypanosoma brucei nucleoside transporter. Mol. Pharmacol. 71:921–929 - PubMed
-
- Balasegaram M., et al. 2009. Effectiveness of melarsoprol and eflornithine as first-line regimens for gambiense sleeping sickness in nine Médecins Sans Frontières programmes. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 103:280–290 - PubMed
-
- Barrett M. P., Zhang Z. Q., Denise H., Giroud C., Baltz T. 1995. A diamidine-resistant Trypanosoma equiperdum clone contains a P2 purine transporter with reduced substrate affinity. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 73:223–229 - PubMed
-
- Barrett M. P., Fairlamb A. H. 1999. The biochemical basis of arsenical-diamidine crossresistance in African trypanosomes. Parasitol. Today 15:136–140 - PubMed
-
- Barrett M. P., et al. 2003. The trypanosomiases. Lancet 362:1469–1480 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

