Sesame oil prevents acute kidney injury induced by the synergistic action of aminoglycoside and iodinated contrast in rats
- PMID: 21402854
- PMCID: PMC3101432
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01597-10
Sesame oil prevents acute kidney injury induced by the synergistic action of aminoglycoside and iodinated contrast in rats
Abstract
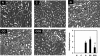
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of sesame oil on acute kidney injury induced by the synergistic action of aminoglycoside and iodinated contrast in rats. Acute kidney injury was induced by a 5-day course of daily gentamicin injections (100 mg/kg of body weight, subcutaneously) and then iodinated contrast (4 ml/kg, intravenously) in male specific-pathogen-free Sprague-Dawley rats. Sesame oil (0.5 ml/kg, orally) was given 1 h before iodinated contrast. Renal function and oxidative stress were assessed 6 h after iodinated contrast injection. Renal function was evaluated by measuring serum blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels. Renal oxidative stress was assessed by determining renal lipid peroxidation, myeloperoxidase, hydroxyl radical, superoxide anion, nitrite/nitrate, and inducible nitric oxide synthase levels. Sesame oil significantly prevented the rise of serum blood urea nitrogen and creatinine levels. Furthermore, there was a parallel inhibition of the rise in levels of expression of renal lipid peroxidation, myeloperoxidase, hydroxyl radicals, superoxide anion, nitrite/nitrate, and inducible nitric oxide synthase in rats with gentamicin-plus-iodinated contrast-induced acute kidney injury. We conclude that sesame oil may attenuate aminoglycoside-plus-iodinated contrast-induced acute kidney injury by inhibiting renal oxidative stress in rats.
Figures
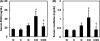
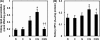
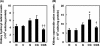
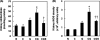
References
-
- Bakris G., Lass N., Gaber A., Jones J., Burnett J. 1990. Radiocontrast medium-induced declines in renal function: a role for oxygen-free radicals. Am. J. Physiol. 258:F115–F120 - PubMed
-
- Bakris G., Lass N., Glock D. 1999. Renal hemodynamics in radiocontrast medium-induced renal dysfunction: a role for dopamine-1 receptors. Kidney Int. 56:206–210 - PubMed
-
- Cetin M., et al. 2008. Ionic high-osmolar contrast medium causes oxidant stress in kidney tissue: partial protective role of ascorbic acid. Ren. Fail. 30:567–572 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

