Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on cartilage apoptosis signalling pathways in ovariectomised rats
- PMID: 21404022
- PMCID: PMC3224622
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1245-3
Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on cartilage apoptosis signalling pathways in ovariectomised rats
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of exposure to pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) on modulation of the cartilage apoptosis signalling pathway in ovariectomised rats by monitoring the expression of mRNA of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) and Bax.
Methods: Forty-eight female Sprague-Dawley rats (250 ± 50 g) were randomly assigned to one of four groups: ovariectomy with PEMF treatment (PEMF group), ovariectomy with oestradiol (E2) treatment (oestrogen group), ovariectomy control (OVX group) and sham group. The ovariectomy model was prepared by surgical resection of the ovaries. After a three-month intermission, animals in the PEMF and oestrogen groups received treatment for 30 days; then serum 17β-oestradiol levels, chondrocyte morphology, and XIAP and Bax mRNA expression in knee joint cartilage were analysed.
Results: The results showed different chondrocyte formation in each group. Serum E2 content in the PEMF and oestrogen groups was significantly higher than in the OVX group (p < 0.05). The expression of XIAP mRNA in the PEMF and oestrogen groups was significantly up-regulated compared to the OVX group, while that of Bax mRNA was significantly down-regulated (p < 0.05). The correlation between E2 level and expression of Bax mRNA was positive (0.506) and statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that PEMF can up-regulate XIAP mRNA expression and down-regulate Bax mRNA expression in ovariectomised rats. Changes in XIAP and Bax mRNA expression may be the mechanism by which PEMF therapy affects postmenopausal osteoarthritis.
Figures

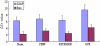

References
-
- Cecil RL, Archer BH. Classification and treatment of chronic arthritis. JAMA. 1992;87:741–746.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

