Is there evidence for a superior method of socket fixation in hip arthroplasty? A systematic review
- PMID: 21404024
- PMCID: PMC3167434
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1234-6
Is there evidence for a superior method of socket fixation in hip arthroplasty? A systematic review
Abstract
Purpose: Total hip arthroplasty has been a very succesful orthopaedic procedure. The optimal fixation method of the acetabular component however, has not yet been defined.
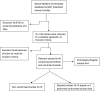
Methods: We performed a systematic review using the Medline and Embase databases to find evidence for the superiority of cemented or cementless acetabular components on short- and long-term clinical and radiological parameters. Methodological quality for randomised trials was assessed using the van Tulder checklist, and for the non randomised studies we used the Newcastle-Ottawa quality assessment scale.
Results: Our search strategy revealed 16 randomised controlled trials (RCT) and 19 non RCT studies in which cemented and cementless acetabular components are compared. A best evidence analysis for complications, wear, osteolysis, migration and clinical scores showed no superiority for either cemented or cementless socket in the RCTs. A best evidence analysis for non RCT studies revealed better osteolysis, migration properties and aseptic loosening survival for cementless sockets; however, wear and overall survival favoured the cemented sockets.
Conclusions: We recommend that an orthopaedic surgeon should choose an established cemented or cementless socket for hip replacement based on patient characteristics, knowledge, experience and preference.
Figures
References
-
- Eskelinen A, Remes V, Helenius I, Pulikkinen P, Nevalainen J, Paavolainen P. Total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthrosis in younger patients in the Finnish arthroplasty register. 4,661 primary replacements followed 0–22 years. Acta Orthop Scand. 2005;76:28–41. doi: 10.1080/00016470510030292. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Callaghan JJ, Templeton JE, Liu SS, Pedersen DR, Goetz DD, Sullivan PM, Johnston RC. Results of Charnley total hip arthroplasty at a minimum of thirty years. A concise follow-up of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86:690–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical