Mediterranean diet supplemented with coenzyme Q10 induces postprandial changes in p53 in response to oxidative DNA damage in elderly subjects
- PMID: 21404051
- PMCID: PMC3312623
- DOI: 10.1007/s11357-011-9229-1
Mediterranean diet supplemented with coenzyme Q10 induces postprandial changes in p53 in response to oxidative DNA damage in elderly subjects
Abstract
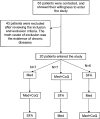
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ) is a powerful antioxidant that reduces oxidative stress. We explored whether the quality of dietary fat alters postprandial oxidative DNA damage and whether supplementation with CoQ improves antioxidant capacity by modifying the activation/stabilization of p53 in elderly subjects. In this crossover study, 20 subjects were randomly assigned to receive three isocaloric diets during 4 weeks each: (1) Mediterranean diet (Med diet), (2) Mediterranean diet supplemented with CoQ (Med+CoQ diet), and (3) saturated fatty acid-rich diet (SFA diet). Levels of mRNAs were determined for p53, p21, p53R2, and mdm2. Protein levels of p53, phosphorylated p53 (Ser20), and monoubiquitinated p53 were also measured, both in cytoplasm and nucleus. The extent of DNA damage was measured as plasma 8-OHdG. SFA diet displayed higher postprandial 8-OHdG concentrations, p53 mRNA and monoubiquitinated p53, and lower postprandial Mdm2 mRNA levels compared with Med and Med+CoQ diets (p < 0.05). Moreover, Med+CoQ diet induced a postprandial decrease of cytoplasmatic p53, nuclear p-p53 (Ser20), and nuclear and cytoplasmatic monoubiquitinated p53 protein (p < 0.05). In conclusion, Med+CoQ diet improves oxidative DNA damage in elderly subjects and reduces processes of cellular oxidation. Our results suggest a starting point for the prevention of oxidative processes associated with aging.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
