Structure and functions of powerful transactivators: VP16, MyoD and FoxA
- PMID: 21404180
- PMCID: PMC3419751
- DOI: 10.1387/ijdb.103194hh
Structure and functions of powerful transactivators: VP16, MyoD and FoxA
Abstract
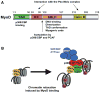
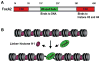
Induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology is a promising approach for converting one type of a differentiated cell into another type of differentiated cell through a pluripotent state as an intermediate step. Recent studies, however, indicate the possibility of directly converting one cell type to another without going through a pluripotent state. This direct reprogramming approach is dependent on a combination of highly potent transcription factors for cell-type conversion, presumably skipping more physiological and multi-step differentiation processes. A trial-and-error strategy is commonly used to screen many candidate transcription factors to identify the correct combination of factors. We speculate, however, that a better understanding of the functional mechanisms of exemplary transcriptional activators will facilitate the identification of novel factor combinations capable of direct reprogramming. The purpose of this review is to critically examine the literature on three highly potent transcriptional activators: the herpes virus protein, VP16; the master regulator of skeletal muscle differentiation, MyoD and the "pioneer" factor for hepatogenesis, FoxA. We discuss the roles of their functional protein domains, interacting partners and chromatin remodeling mechanisms during gene activation to understand how these factors open the chromatin of inactive genes and reset the transcriptional pattern during cell type conversion.
Figures

References
-
- BERKES CA, BERGSTROM DA, PENN BH, SEAVER KJ, KNOEPFLER PS, TAPSCOTT SJ. Pbx marks genes for activation by MyoD indicating a role for a homeodomain protein in establishing myogenic potential. Mol Cell. 2004;14:465–477. - PubMed
-
- BERKES CA, TAPSCOTT SJ. MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005;16:585–595. - PubMed
-
- BOSSARD P, ZARET KS. GATA transcription factors as potentiators of gut endoderm differentiation. Development. 1998;125:4909–4917. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

