Comparative analysis of oncogenic genes revealed unique evolutionary features of field Marek's disease virus prevalent in recent years in China
- PMID: 21406076
- PMCID: PMC3068976
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-8-121
Comparative analysis of oncogenic genes revealed unique evolutionary features of field Marek's disease virus prevalent in recent years in China
Abstract
Background: Marek's disease (MD) is an economically important viral disease of chickens caused by Marek's disease virus (MDV), an oncogenic herpesvirus. This disease was well controlled since the widespread use of commercial vaccines, but field MDVs have shown continuous increasing in virulence and acquired the ability to overcome the immune response induced by vaccines. Nowadays, MD continues to be a serious threat to poultry industry, isolation and characterization of MDVs are essential for monitoring changes of viruses and evaluating the effectiveness of existing vaccines.
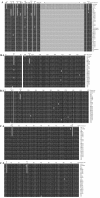
Results: Between 2008 and 2010, 18 field MDV strains were isolated from vaccinated chicken flocks in Sichuan province, China. Three oncogenic genes including Meq, pp38 and vIL-8 genes of the 18 isolates were amplified and sequenced. Homology analysis showed that the deduced amino acid sequences of these three genes exhibit 95.0-98.8%, 99.3-100% and 97.0-98.5% homology respectively with these of other reference strains published in GenBank. Alignment analysis of the nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences showed that four amino acid mutations in Meq gene and two amino acid mutations in vIL-8 gene displayed perfect regularity in MDVs circulating in China, which could be considered as features of field MDVs prevalent in recent years in China. In addition, one amino acid mutation in pp38 gene can be considered as a feature of virulent MDVs from USA, and three amino acid mutations in Meq gene were identified and unique in very virulent plus (vv+) MDVs. Phylogenetic analysis based on Meq and vIL-8 protein sequences revealed that field MDVs in China evolved independently. Virulence studies showed that CVI988 could provide efficient protection against the field MDVs epidemic recently in China.
Conclusions: This study and other published data in the GenBank have demonstrated the features of Meq, pp38 and vIL-8 genes of MDVs circulating in recent years in Sichuan, China. Mutations, deletions or insertions were observed in these three genes, and some mutations could be considered as the unique marks of the MDVs circulating presently in China. The paper supplies some valuable information concerning the evolution of MDV which is useful for the vaccine development and control of MD in China.
Figures


References
-
- Calnek BW. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease virus infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2001;255:25–55. - PubMed
-
- Shek WR, Calnek BW, Schat KA, Chen CH. Characterization of Marek's disease virus-infected lymphocytes: discrimination between cytolytically and latently infected cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983;70:485–491. - PubMed
-
- Bulow VV, Biggs PM. Differentiation between strains of Marek's disease virus and turkey herpesvirus by immunofluorescence assays. Avian Pathol. 1975;4:133–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

