Randomized controlled trials of malaria intervention trials in Africa, 1948 to 2007: a descriptive analysis
- PMID: 21406113
- PMCID: PMC3064642
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-61
Randomized controlled trials of malaria intervention trials in Africa, 1948 to 2007: a descriptive analysis
Abstract
Background: Nine out of ten deaths from malaria occur in sub-Saharan Africa. Various control measures have achieved some progress in the control of the disease, but malaria is still a major public health problem in Africa. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are universally considered the best study type to rigorously assess whether an intervention is effective. The study reported here provides a descriptive analysis of RCTs reporting interventions for the prevention and treatment of malaria conducted in Africa, with the aim of providing detailed information on their main clinical and methodological characteristics, that could be used by researchers and policy makers to help plan future research.
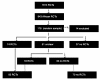
Methods: Systematic searches for malaria RCTs were conducted using electronic databases (Medline, Embase, the Cochrane Library), and an African geographic search filter to identify RCTs conducted in Africa was applied. Results were exported to the statistical package STATA 8 to obtain a random sample from the overall data set. Final analysis of trial characteristics was done in a double blinded fashion by two authors using a standardized data extraction form.
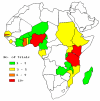
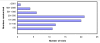
Results: A random sample of 92 confirmed RCTs (from a total of 943 reports obtained between 1948 and 2007) was prepared. Most trials investigated drug treatment in children with uncomplicated malaria. Few trials reported on treatment of severe malaria or on interventions in pregnant women. Most trials were of medium size (100-500 participants), individually randomized and based in a single centre. Reporting of trial quality was variable. Although three-quarter of trials provided information on participants' informed consent and ethics approval, more details are needed.
Conclusions: The majority of malaria RCT conducted in Africa report on drug treatment and prevention in children; there is need for more research done in pregnant women. Sources of funding, informed consent and trial quality were often poorly reported. Overall, clearer reporting of trials is needed.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. World malaria report. Geneva. 2009. http://www.who.int/malaria/world_malaria_report_2009/en/
-
- O'Meara WP, Mangeni JN, Steketee R, Greenwood B. Changes in the burden of malaria in sub-Saharan Africa. Lancet Infect Dis. 2010;10:545–555. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical