Requirement of Osteopontin in the migration and protection against Taxol-induced apoptosis via the ATX-LPA axis in SGC7901 cells
- PMID: 21406114
- PMCID: PMC3068946
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2121-12-11
Requirement of Osteopontin in the migration and protection against Taxol-induced apoptosis via the ATX-LPA axis in SGC7901 cells
Abstract
Background: Autotaxin (ATX) possesses lysophospholipase D (lyso PLD) activity, which converts lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) into lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). The ATX-LPA signaling axis has been implicated in angiogenesis, chronic inflammation and tumor progression. Osteopontin (OPN) is an important chemokine involved in the survival, proliferation, migration, invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells. The focus of the present study was to investigate the relationship between the ATX-LPA axis and OPN.
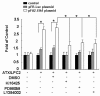
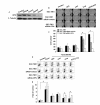
Results: In comparison with non-treated cells, we found that the ATX-LPA axis up-regulated OPN expression by 1.92-fold in protein levels and 1.3-fold in mRNA levels. The ATX-LPA axis activates LPA2, Akt, ERK and ELK-1 and also protects SGC7901 cells from apoptosis induced by Taxol treatment.
Conclusions: This study provides the first evidence that expression of OPN induced by ATX-LPA axis is mediated by the activation of Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways through the LPA2 receptor. In addition, OPN is required for the protective effects of ATX-LPA against Taxol-induced apoptosis and ATX-LPA-induced migration of SGC7901 cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ATX-LPA axis induces expression of OPN in hepatic cancer cell SMMC7721.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011 Mar;294(3):406-11. doi: 10.1002/ar.21324. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21337710
-
Autotaxin signaling via lysophosphatidic acid receptors contributes to vascular endothelial growth factor-induced endothelial cell migration.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Mar;8(3):309-21. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0288. Epub 2010 Mar 2. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20197381 Free PMC article.
-
Autotaxin is induced by TSA through HDAC3 and HDAC7 inhibition and antagonizes the TSA-induced cell apoptosis.Mol Cancer. 2011 Feb 12;10:18. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-18. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21314984 Free PMC article.
-
ATX-LPA receptor axis in inflammation and cancer.Cell Cycle. 2009 Nov 15;8(22):3695-701. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.22.9937. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19855166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation and biological activities of the autotaxin-LPA axis.Prog Lipid Res. 2007 Mar;46(2):145-60. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2007.02.001. Epub 2007 Mar 16. Prog Lipid Res. 2007. PMID: 17459484 Review.
Cited by
-
Migration of gastric cancer cells in response to lysophosphatidic acid is mediated by LPA receptor 2.Oncol Lett. 2013 Mar;5(3):1048-1052. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1107. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23426604 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid phosphate phosphatases and their roles in mammalian physiology and pathology.J Lipid Res. 2015 Nov;56(11):2048-60. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R058362. Epub 2015 Mar 26. J Lipid Res. 2015. PMID: 25814022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in targeting the autotaxin-lysophosphatidate-lipid phosphate phosphatase axis in vivo.J Biomed Res. 2016 Jul;30(4):272-84. doi: 10.7555/JBR.30.20150058. Epub 2015 Aug 28. J Biomed Res. 2016. PMID: 27533936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Insights and Clinical Implications of ELK1 in Solid Tumors: A Narrative Review.Cells. 2025 Aug 14;14(16):1257. doi: 10.3390/cells14161257. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40862737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid induces the migration and invasion of SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells through the LPA2 and Notch signaling pathways.Int J Mol Med. 2019 Jul;44(1):67-78. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4186. Epub 2019 May 8. Int J Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31115486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fang X, Schummer M, Mao M. Lysophosphatidic acid is a bioactive mediator in ovarian cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1582:257–64. - PubMed
-
- Umezu-Goto M, Kishi Y, Taira A, Hama K, Dohmae N, Takio K, Yamori T, Mills GB, Inoue K, Aoki J, Arai H. Autotaxin has lysophospholipase D activity leading to tumor cell growth and motility by lysophosphatidic acid production. J Cell Biol. 2002;158(2):227–33. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200204026. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

