Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway in breast cancer
- PMID: 21406469
- PMCID: PMC3228119
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0402
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway in breast cancer
Abstract
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) network plays a key regulatory function in cell survival, proliferation, migration, metabolism, angiogenesis, and apoptosis. Genetic aberrations found at different levels, either with activation of oncogenes or inactivation of tumor suppressors, make this pathway one of the most commonly disrupted in human breast cancer. The PI3K-dependent phosphorylation and activation of the serine/threonine kinase AKT is a key activator of cell survival mechanisms. The activation of the oncogene PIK3CA and the loss of regulators of AKT including the tumor suppressor gene PTEN are mutations commonly found in breast tumors. AKT relieves the negative regulation of mTOR to activate protein synthesis and cell proliferation through S6K and 4EBP1. The common activation of the PI3K pathway in breast cancer has led to the development of compounds targeting the effector mechanisms of the pathway including selective and pan-PI3K/pan-AKT inhibitors, rapamycin analogs for mTOR inhibition, and TOR-catalytic subunit inhibitors. The influences of other oncogenic pathways such as Ras-Raf-Mek on the PI3K pathway and the known feedback mechanisms of activation have prompted the use of compounds with broader effect at multiple levels and rational combination strategies to obtain a more potent antitumor activity and possibly a meaningful clinical effect. Here, we review the biology of the network, its role in the development and progression of breast cancer, and the evaluation of targeted therapies in clinical trials.
Conflict of interest statement
Section Editor
Section Editor
Reviewer “A” discloses no financial relationships.
The content of this article has been reviewed by independent peer reviewers to ensure that it is balanced, objective, and free from commercial bias. On the basis of disclosed information, all conflicts of interest have been resolved.
Figures
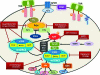
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100:57–70. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ. The Pezcoller lecture: cancer cell cycles revisited. Cancer Res. 2000;60:3689–3695. - PubMed
-
- Chang HW, Aoki M, Fruman D, et al. Transformation of chicken cells by the gene encoding the catalytic subunit of PI 3-kinase. Science. 1997;276:1848–1850. - PubMed
-
- Hoeflich KP, O'Brien C, Boyd Z, et al. In vivo antitumor activity of MEK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors in basal-like breast cancer models. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:4649–4664. - PubMed
-
- Samuels Y, Ericson K. Oncogenic PI3K and its role in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18:77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

