ARF1 localizes to the golgi and the trans-golgi network
- PMID: 21406621
- PMCID: PMC3082265
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.110.082099
ARF1 localizes to the golgi and the trans-golgi network
Figures
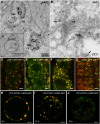
Comment on
-
The multivesicular body-localized GTPase ARFA1b/1c is important for callose deposition and ROR2 syntaxin-dependent preinvasive basal defense in barley.Plant Cell. 2010 Nov;22(11):3831-44. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.078063. Epub 2010 Nov 5. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 21057060 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balderhaar H.J., Arlt H., Ostrowicz C., Bröcker C., Sündermann F., Brandt R., Babst M., Ungermann C. (2010). The Rab GTPase Ypt7 is linked to retromer-mediated receptor recycling and fusion at the yeast late endosome. J. Cell Sci. 123: 4085–4094 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

