Determinants of dwell time in visual search: similarity or perceptual difficulty?
- PMID: 21408139
- PMCID: PMC3050928
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017740
Determinants of dwell time in visual search: similarity or perceptual difficulty?
Abstract
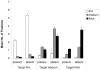
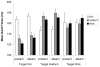
The present study examined the factors that determine the dwell times in a visual search task, that is, the duration the gaze remains fixated on an object. It has been suggested that an item's similarity to the search target should be an important determiner of dwell times, because dwell times are taken to reflect the time needed to reject the item as a distractor, and such discriminations are supposed to be harder the more similar an item is to the search target. In line with this similarity view, a previous study shows that, in search for a target ring of thin line-width, dwell times on thin linewidth Landolt C's distractors were longer than dwell times on Landolt C's with thick or medium linewidth. However, dwell times may have been longer on thin Landolt C's because the thin line-width made it harder to detect whether the stimuli had a gap or not. Thus, it is an open question whether dwell times on thin line-width distractors were longer because they were similar to the target or because the perceptual decision was more difficult. The present study de-coupled similarity from perceptual difficulty, by measuring dwell times on thin, medium and thick line-width distractors when the target had thin, medium or thick line-width. The results showed that dwell times were longer on target-similar than target-dissimilar stimuli across all target conditions and regardless of the line-width. It is concluded that prior findings of longer dwell times on thin linewidth-distractors can clearly be attributed to target similarity. As will be discussed towards the end, the finding of similarity effects on dwell times has important implications for current theories of visual search and eye movement control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Treisman A, Gelade G. A feature integration theory of attention. Cogn Psych. 1980;12:97–136. - PubMed
-
- Zelinsky GJ. Using eye saccades to assess the selectivity of search movements. Vis Res. 1996;36:2177–2187. - PubMed
-
- Zelinksy GJ, Sheinberg DL. Eye movements during parallel-serial visual search. JEP-HPP. 1997;23:244–262. - PubMed
-
- Shen J, Reingold EM, Pomplun M, Williams, DE Hyona J, Radach R, Deubel H, editors. Saccadic selectivity during visual search: The influence of central processing difficulty. The mind's eyes: Cognitive and applied aspects of eye movement research. Elsevier Science Publishers. 2003. pp. 65–88.
-
- Hooge ITC, Erkelens CJ. Control of fixation duration in a simple search task. Percept & Psychophys. 1996;58:969–976. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

