Functional role of glutamine 28 and arginine 39 in double stranded RNA cleavage by human pancreatic ribonuclease
- PMID: 21408145
- PMCID: PMC3050822
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017159
Functional role of glutamine 28 and arginine 39 in double stranded RNA cleavage by human pancreatic ribonuclease
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2011;6(4). doi:10.1371/annotation/68ded407-ac40-47b5-b3d7-966e116a28b2
Abstract
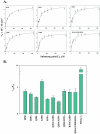
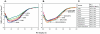
Human pancreatic ribonuclease (HPR), a member of RNase A superfamily, has a high activity on double stranded (ds) RNA. By virtue of this activity HPR appears to be involved in the host-defense against pathogenic viruses. To delineate the mechanism of dsRNA cleavage by HPR, we have investigated the role of glutamine 28 and arginine 39 of HPR in its activity on dsRNA. A non-basic residue glycine 38, earlier shown to be important for dsRNA cleavage by HPR was also included in the study in the context of glutamine 28 and arginine 39. Nine variants of HPR respectively containing Q28A, Q28L, R39A, G38D, Q28A/R39A, Q28L/R39A, Q28A/G38D, R39A/G38D and Q28A/G38D/R39A mutations were generated and functionally characterized. The far-UV CD-spectral analysis revealed all variants, except R39A, to have structures similar to that of HPR. The catalytic activity of all HPR variants on single stranded RNA substrate was similar to that of HPR, whereas on dsRNA, the catalytic efficiency of all single residue variants, except for the Q28L, was significantly reduced. The dsRNA cleavage activity of R39A/G38D and Q28A/G38D/R39A variants was most drastically reduced to 4% of that of HPR. The variants having reduced dsRNA cleavage activity also had reduction in their dsDNA melting activity and thermal stability. Our results indicate that in HPR both glutamine 28 and arginine 39 are important for the cleavage of dsRNA. Although these residues are not directly involved in catalysis, both arginine 39 and glutamine 28 appear to be facilitating a productive substrate-enzyme interaction during the dsRNA cleavage by HPR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Glycine 38 is crucial for the ribonucleolytic activity of human pancreatic ribonuclease on double-stranded RNA.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Sep 20;297(2):390-5. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02216-7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 12237131
-
Degradation of double-stranded RNA by human pancreatic ribonuclease: crucial role of noncatalytic basic amino acid residues.Biochemistry. 2003 Sep 2;42(34):10182-90. doi: 10.1021/bi030040q. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12939146
-
Role of unique basic residues of human pancreatic ribonuclease in its catalysis and structural stability.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Sep 7;360(4):809-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.06.141. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17631275
-
Structural basis for non-catalytic and catalytic activities of ribonuclease III.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Aug;62(Pt 8):933-40. doi: 10.1107/S090744490601153X. Epub 2006 Jul 18. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006. PMID: 16855311 Review.
-
Integration of kinetic isotope effect analyses to elucidate ribonuclease mechanism.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Nov;1854(11):1801-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.04.022. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25936517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Purification and characterization of RGA2, a Rho2 GTPase-activating protein from Tinospora cordifolia.3 Biotech. 2016 Jun;6(1):85. doi: 10.1007/s13205-016-0400-3. Epub 2016 Mar 1. 3 Biotech. 2016. PMID: 28330155 Free PMC article.
-
Insight of the Interaction between 2,4-thiazolidinedione and Human Serum Albumin: A Spectroscopic, Thermodynamic and Molecular Docking Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 3;20(11):2727. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112727. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31163649 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical characterization of CTX-M-15 from Enterobacter cloacae and designing a novel non-β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056926. Epub 2013 Feb 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23437273 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic analysis of Cas12a and Cas13a RNA-Guided nucleases for development of improved CRISPR-Based diagnostics.iScience. 2021 Aug 18;24(9):102996. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102996. eCollection 2021 Sep 24. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34505008 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Amylase and Alpha-Glucosidase Enzyme Inhibition and Antioxidant Potential of 3-Oxolupenal and Katononic Acid Isolated from Nuxia oppositifolia.Biomolecules. 2019 Dec 30;10(1):61. doi: 10.3390/biom10010061. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31905962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beintema JJ, Breukelman HJ, Carsana A, Furia A. Evolution of vertebrateribonucleases: Ribonuclease A superfamily. In: D'Alessio G, Riordin JF, editors. Ribonucleases: Structures and Functions. New York: Academic; 1997. pp. 245–69.
-
- Libonati M, Sorrentino S. Degradation of double-stranded RNA by mammalian pancreatic-type ribonucleases. Methods Enzymol. 2001;341:234–248. - PubMed
-
- Sorrentino S, Libonati M. Structure-function relationships in human ribonucleases: main distinctive features of the major RNase types. FEBS Lett. 1997;404:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Sorrentino S, Libonati M. Human pancreatic type and nonpancreatic type ribonucleases: A direct side-by-side comparison of their catalytic properties. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;312:340–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

