A bow-tie genetic architecture for morphogenesis suggested by a genome-wide RNAi screen in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 21408209
- PMCID: PMC3048373
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002010
A bow-tie genetic architecture for morphogenesis suggested by a genome-wide RNAi screen in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
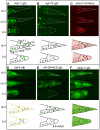
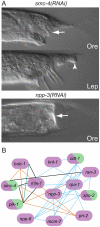
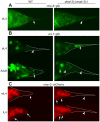
During animal development, cellular morphogenesis plays a fundamental role in determining the shape and function of tissues and organs. Identifying the components that regulate and drive morphogenesis is thus a major goal of developmental biology. The four-celled tip of the Caenorhabditis elegans male tail is a simple but powerful model for studying the mechanism of morphogenesis and its spatiotemporal regulation. Here, through a genome-wide post-embryonic RNAi-feeding screen, we identified 212 components that regulate or participate in male tail tip morphogenesis. We constructed a working hypothesis for a gene regulatory network of tail tip morphogenesis. We found regulatory roles for the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3, the TGF-β pathway, nuclear hormone receptors (e.g. nhr-25), the heterochronic gene blmp-1, and the GATA transcription factors egl-18 and elt-6. The majority of the pathways converge at dmd-3 and mab-3. In addition, nhr-25 and dmd-3/mab-3 regulate each others' expression, thus placing these three genes at the center of a complex regulatory network. We also show that dmd-3 and mab-3 negatively regulate other signaling pathways and affect downstream cellular processes such as vesicular trafficking (e.g. arl-1, rme-8) and rearrangement of the cytoskeleton (e.g. cdc-42, nmy-1, and nmy-2). Based on these data, we suggest that male tail tip morphogenesis is governed by a gene regulatory network with a bow-tie architecture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Sulston JE, Albertson DG, Thomson JN. The Caenorhabditis elegans male: postembryonic development of nongonadal structures. Dev Biol. 1980;78:542–576. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen CQ, Hall DH, Yang Y, Fitch DH. Morphogenesis of the Caenorhabditis elegans male tail tip. Dev Biol. 1999;207:86–106. - PubMed
-
- Sulston JE, Horvitz HR. Post-embryonic cell lineages of the nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1977;56:110–156. - PubMed
-
- Zhao X, Yang Y, Fitch DH, Herman MA. TLP-1 is an asymmetric cell fate determinant that responds to Wnt signals and controls male tail tip morphogenesis in C. elegans. Development. 2002;129:1497–1508. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

