Signal pathways in astrocytes activated by cross-talk between of astrocytes and mast cells through CD40-CD40L
- PMID: 21410936
- PMCID: PMC3068960
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-25
Signal pathways in astrocytes activated by cross-talk between of astrocytes and mast cells through CD40-CD40L
Abstract
Background: Astrocytes, which play an active role in chronic inflammatory diseases like multiple sclerosis, exist close to mast cells with which they share perivascular localization. We previously demonstrated the possibility that astrocytes and mast cells interact in vitro and in vivo. This study aimed to investigate the signaling pathways and the role for astrocytes in the interaction of astrocytes and mast cells.
Methods: We co-cultured human U87 glioblastoma (U87) and human mast cell-1 (HMC-1) cell lines, and mouse cerebral cortices-derived astrocytes and mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (BMMCs). Intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) was measured by confocal microscopy; CD40 siRNA by Silencer Express Kit; small GTPases by GTP-pull down assay; PKCs, MAPKs, CD40, CD40L, Jak1/2, STAT1, TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) by Western blot; NF-κB and AP-1 by EMSA; cytokines by RT-PCR. An experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) model was induced using myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) peptide and pertussis toxin in mice. Co-localization of TNFR1 and astrocytes in EAE brain tissues was determined by immunohistochemistry.
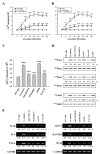
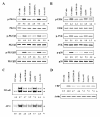
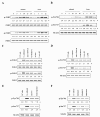
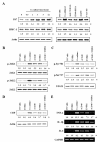
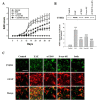
Results: Each astrocyte co-culture had increases in [Ca2+]i levels, release of cytokines and chemokines; activities of Rho-family GTPases, NF-κB/AP-1/STAT1727, and Jack1/2, STAT1701. These effects were inhibited by anti-CD40 antibody or CD40 siRNA, and signaling pathways for Jak1/2 were inhibited by anti-TNFR1 antibody. EAE score, expression of TNFR1, and co-localization of TNFR1 and astrocytes were enhanced in brain of the EAE model. Anti-CD40 antibody or 8-oxo-dG pretreatment reduced these effects in EAE model.
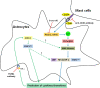
Conclusions: These data suggest that astrocytes activated by the CD40-CD40L interaction in co-culture induce inflammatory cytokine production via small GTPases, and the secreted cytokines re-activate astrocytes via Jak/STAT1701 pathways, and then release more cytokines that contribute to exacerbating the development of EAE. These findings imply that the pro-inflammatory mediators produced by cell-to-cell cross-talk via interaction of CD40-CD40L may be as a promising therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases like MS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signaling pathways in the activation of mast cells cocultured with astrocytes and colocalization of both cells in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.J Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;185(1):273-83. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1000991. Epub 2010 May 28. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20511559
-
IgE production in CD40/CD40L cross-talk of B and mast cells and mediator release via TGase 2 in mouse allergic asthma.Cell Signal. 2013 Jun;25(6):1514-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23524335
-
CD1d expressed in mast cell surface enhances IgE production in B cells by up-regulating CD40L expression and mediator release in allergic asthma in mice.Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):1105-17. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.029. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24509414
-
Messages in CD40L are encrypted for residue-specific functions.Cytokine. 2025 Jan;185:156824. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156824. Epub 2024 Nov 30. Cytokine. 2025. PMID: 39615244 Review.
-
The CD40/CD40 ligand dyad and its downstream effector molecule ISG54 in relating acute neuroinflammation with persistent, progressive demyelination.IUBMB Life. 2024 Jun;76(6):313-331. doi: 10.1002/iub.2798. Epub 2023 Dec 20. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 38116887 Review.
Cited by
-
Interferon-α regulates glutaminase 1 promoter through STAT1 phosphorylation: relevance to HIV-1 associated neurocognitive disorders.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e32995. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032995. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479354 Free PMC article.
-
An integrative characterization of recurrent molecular aberrations in glioblastoma genomes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Oct;41(19):8803-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt656. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23907387 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance and Control of Low-Grade Inflammation Due to Damage of Cellular Barrier Systems That May Lead to Systemic Inflammation.Front Neurol. 2019 May 29;10:533. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00533. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31191433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-Talk between Glia, Neurons and Mast Cells in Neuroinflammation Associated with Parkinson's Disease.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018 Mar;13(1):100-112. doi: 10.1007/s11481-017-9766-1. Epub 2017 Sep 26. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28952015 Free PMC article.
-
Topical cathelicidin (LL-37) an innate immune peptide induces acute olfactory epithelium inflammation in a mouse model.Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015 Dec;5(12):1141-50. doi: 10.1002/alr.21634. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015. PMID: 26346056 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

