Molecular and virulence characteristics of an outer membrane-associated RTX exoprotein in Pasteurella pneumotropica
- PMID: 21410992
- PMCID: PMC3075217
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-55
Molecular and virulence characteristics of an outer membrane-associated RTX exoprotein in Pasteurella pneumotropica
Abstract
Background: Pasteurella pneumotropica is a ubiquitous bacterium that is frequently isolated from laboratory rodents and causes various clinical symptoms in immunodeficient animals. Currently two RTX toxins, PnxIA and PnxIIA, which are similar to hemolysin-like high-molecular-weight exoproteins are known in this species. In this study, we identified and analyzed a further RTX toxin named PnxIIIA and the corresponding type I secretion system.
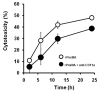
Results: The RTX exoprotein, PnxIIIA, contains only a few copies of the RTX repeat-like sequence and 3 large repeat sequences that are partially similar to the outer membrane protein found in several prokaryotes. Recombinant PnxIIIA protein (rPnxIIIA) was cytotoxic toward J774A.1 mouse macrophage cells, whereas cytotoxicity was attenuated by the addition of anti-CD11a monoclonal antibody. rPnxIIIA could bind to extracellular matrices (ECMs) and cause hemagglutination of sheep erythrocytes. Binding was dependent on the 3 large repeat sequences in PnxIIIA. Protein interaction analyses indicated that PnxIIIA is mainly localized in the outer membrane of P. pneumotropica ATCC 35149 in a self-assembled oligomeric form. PnxIIIA is less cytotoxic to J774A.1 cells than PnxIA and PnxIIA.
Conclusions: The results implicate that PnxIIIA is located on the cell surface and participates in adhesion to ECMs and enhanced hemagglutination in the rodent pathogen P. pneumotropica.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of hemolysin-like proteins similar to RTX toxin in Pasteurella pneumotropica.J Bacteriol. 2009 Jun;191(11):3698-705. doi: 10.1128/JB.01527-08. Epub 2009 Apr 10. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19363112 Free PMC article.
-
From the [Pasteurella] pneumotropica complex to Rodentibacter spp.: an update on [Pasteurella] pneumotropica.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Apr;217:121-134. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.03.011. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29615244 Review.
-
Intranasal immunization with a non-adjuvanted adhesive protein descended from Pasteurella pneumotropica and its preventive efficacy against opportunistic infection in mice.Vaccine. 2013 Nov 19;31(48):5729-35. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.09.033. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 24091313
-
Identification of a virulence determinant that is conserved in the Jawetz and Heyl biotypes of [Pasteurella] pneumotropica.Pathog Dis. 2016 Aug;74(6):ftw066. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftw066. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Pathog Dis. 2016. PMID: 27402782
-
RTX toxins in Pasteurellaceae.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Sep;292(3-4):149-58. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00200. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12398206 Review.
Cited by
-
Ehrlichia chaffeensis tandem repeat proteins and Ank200 are type 1 secretion system substrates related to the repeats-in-toxin exoprotein family.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2011 Dec 30;1:22. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2011.00022. eCollection 2011. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22919588 Free PMC article.
-
The Genomic Sequence of the Oral Pathobiont Strain NI1060 Reveals Unique Strategies for Bacterial Competition and Pathogenicity.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 13;11(7):e0158866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158866. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27409077 Free PMC article.
-
Draft Genome Sequence of the Rodent Opportunistic Pathogen Pasteurella pneumotropica ATCC 35149T.Genome Announc. 2014 Aug 7;2(4):e00771-14. doi: 10.1128/genomeA.00771-14. Genome Announc. 2014. PMID: 25103762 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal Immunization with Nasal Immuno-Inducible Sequence-Fused Antigens Elicits Antigen-Specific Antibody Production.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 28;25(23):12828. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312828. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684539 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of humoral immune responses and pathologies of BALB/c and C57BL/6 wildtype mice experimentally infected with a highly virulent Rodentibacter pneumotropicus (Pasteurella pneumotropica) strain.BMC Microbiol. 2018 May 30;18(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1186-8. BMC Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29848308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Macy JD Jr, Weir EC, Compton SR, Shlomchik MJ, Brownstein DG. Dual infection with Pneumocystis carinii and Pasteurella pneumotropica in B cell-deficient mice: diagnosis and therapy. Comp Med. 2000;50:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Chapes SK, Mosier DA, Wright AD, Hart ML. MHCII, Tlr4 and Nramp1 genes control host pulmonary resistance against the opportunistic bacterium Pasteurella pneumotropica. J Leukoc Biol. 2001;69:381–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

