PrtT-regulated proteins secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus activate MAPK signaling in exposed A549 lung cells leading to necrotic cell death
- PMID: 21412410
- PMCID: PMC3055868
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017509
PrtT-regulated proteins secreted by Aspergillus fumigatus activate MAPK signaling in exposed A549 lung cells leading to necrotic cell death
Abstract
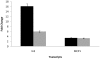
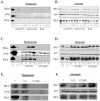
Aspergillus fumigatus is the most commonly encountered mold pathogen of humans, predominantly infecting the respiratory system. Colonization and penetration of the lung alveolar epithelium is a key but poorly understood step in the infection process. This study focused on identifying the transcriptional and cell-signaling responses activated in A549 alveolar carcinoma cells incubated in the presence of A. fumigatus wild-type and ΔPrtT protease-deficient germinating conidia and culture filtrates (CF). Microarray analysis of exposed A549 cells identified distinct classes of genes whose expression is altered in the presence of germinating conidia and CF and suggested the involvement of both NFkB and MAPK signaling pathways in mediating the cellular response. Phosphoprotein analysis of A549 cells confirmed that JNK and ERK1/2 are phosphorylated in response to CF from wild-type A. fumigatus and not phosphorylated in response to CF from the ΔPrtT protease-deficient strain. Inhibition of JNK or ERK1/2 kinase activity substantially decreased CF-induced cell damage, including cell peeling, actin-cytoskeleton damage, and reduction in metabolic activity and necrotic death. These results suggest that inhibition of MAPK-mediated host responses to treatment with A. fumigatus CF decreases cellular damage, a finding with possible clinical implications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptional and proteomic analysis of the Aspergillus fumigatus ΔprtT protease-deficient mutant.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033604. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514608 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Profiles of Human Lung Epithelial Cells A549 Interacting with Aspergillus fumigatus by RNA-Seq.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 14;10(8):e0135720. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135720. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26273834 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and Proteomic Analysis of the Aspergillus fumigatus ΔPrtT, ΔXprG and ΔXprG/ΔPrtT Protease-Deficient Mutants.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 12;8:2490. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02490. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29312198 Free PMC article.
-
β-1,3-Glucan-induced host phospholipase D activation is involved in Aspergillus fumigatus internalization into type II human pneumocyte A549 cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021468. Epub 2011 Jul 8. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21760893 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of secreted Aspergillus fumigatus proteases in disruption of the actin fiber cytoskeleton and loss of focal adhesion sites in infected A549 lung pneumocytes.J Infect Dis. 2004 Jun 1;189(11):1965-73. doi: 10.1086/420850. Epub 2004 May 11. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15143461
Cited by
-
Transcriptional and proteomic analysis of the Aspergillus fumigatus ΔprtT protease-deficient mutant.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e33604. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033604. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514608 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the involvement of cofilin in Aspergillus fumigatus internalization into type II alveolar epithelial cells.BMC Microbiol. 2015 Aug 13;15:161. doi: 10.1186/s12866-015-0500-y. BMC Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26268695 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of Aspergillus fumigatus Conidia with Airway Epithelial Cells: A Critical Review.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 7;7:472. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00472. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27092126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational approaches for discovery of common immunomodulators in fungal infections: towards broad-spectrum immunotherapeutic interventions.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Oct 7;13:224. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-224. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24099000 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Host Pathways Govern Epithelial Cell Invasion of Aspergillus fumigatus.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0008423. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00084-23. Epub 2023 May 31. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37255456 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Denning DW. Invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:781–803; quiz 804–785. - PubMed
-
- Steinbach WJ, Stevens DA. Review of newer antifungal and immunomodulatory strategies for invasive aspergillosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(Suppl 3):S157–187. - PubMed
-
- Segal BH. Aspergillosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1870–1884. - PubMed
-
- Mullins J, Harvey R, Seaton A. Sources and incidence of airborne Aspergillus fumigatus (Fres). Clin Allergy. 1976;6:209–217. - PubMed
-
- Brakhage AA, Bruns S, Thywissen A, Zipfel PF, Behnsen J. Interaction of phagocytes with filamentous fungi. Curr Opin Microbiol. 13:409–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

