Assessment of the frequency-domain multi-distance method to evaluate the brain optical properties: Monte Carlo simulations from neonate to adult
- PMID: 21412461
- PMCID: PMC3047361
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.2.000552
Assessment of the frequency-domain multi-distance method to evaluate the brain optical properties: Monte Carlo simulations from neonate to adult
Abstract
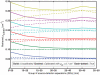
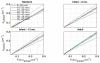
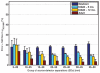
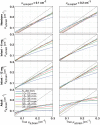
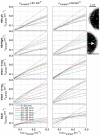
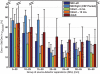
The near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) frequency-domain multi-distance (FD-MD) method allows for the estimation of optical properties in biological tissue using the phase and intensity of radiofrequency modulated light at different source-detector separations. In this study, we evaluated the accuracy of this method to retrieve the absorption coefficient of the brain at different ages. Synthetic measurements were generated with Monte Carlo simulations in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based heterogeneous head models for four ages: newborn, 6 and 12 month old infants, and adult. For each age, we determined the optimal set of source-detector separations and estimated the corresponding errors. Errors arise from different origins: methodological (FD-MD) and anatomical (curvature, head size and contamination by extra-cerebral tissues). We found that the brain optical absorption could be retrieved with an error between 8-24% in neonates and infants, while the error increased to 19-44% in adults over all source-detector distances. The dominant contribution to the error was found to be the head curvature in neonates and infants, and the extra-cerebral tissues in adults.
Keywords: (110.3080) Infrared imaging; (170.3660) Light propagation in tissues; (170.5280) Photon migration.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of Different Optical Properties of Head Tissues on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Using Monte Carlo Simulations.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1395:39-43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-14190-4_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 36527611 Review.
-
Patient-oriented simulation based on Monte Carlo algorithm by using MRI data.Biomed Eng Online. 2012 Apr 17;11:21. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-11-21. Biomed Eng Online. 2012. PMID: 22510474 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of oxygen saturation and total hemoglobin estimates in the neonatal brain using the semi-infinite slab model for FD-NIRS data analysis.Biomed Opt Express. 2014 Nov 14;5(12):4300-12. doi: 10.1364/BOE.5.004300. eCollection 2014 Dec 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2014. PMID: 25574439 Free PMC article.
-
Depth sensitivity analysis of functional near-infrared spectroscopy measurement using three-dimensional Monte Carlo modelling-based magnetic resonance imaging.Lasers Med Sci. 2010 May;25(3):431-8. doi: 10.1007/s10103-010-0754-4. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Lasers Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 20143117
-
Frequency-Domain Techniques for Cerebral and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.Front Neurosci. 2020 Apr 7;14:300. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00300. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32317921 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accuracy of homogeneous models for photon diffusion in estimating neonatal cerebral hemodynamics by TD-NIRS.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Mar 8;12(4):1905-1921. doi: 10.1364/BOE.417357. eCollection 2021 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 33996206 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between neurological examination at term-equivalent age and cerebral hemodynamics and oxygen metabolism in infants born preterm.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 2;17:1105638. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1105638. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36937667 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of tissue oximeters on a liquid phantom with adjustable optical properties: an extension.Biomed Opt Express. 2017 Dec 5;9(1):86-101. doi: 10.1364/BOE.9.000086. eCollection 2018 Jan 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2017. PMID: 29359089 Free PMC article.
-
Optical characterization of two-layered turbid media for non-invasive, absolute oximetry in cerebral and extracerebral tissue.PLoS One. 2013 May 21;8(5):e64095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064095. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724023 Free PMC article.
-
Atlas-based head modeling and spatial normalization for high-density diffuse optical tomography: in vivo validation against fMRI.Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 15;85 Pt 1(0 1):117-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.03.069. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 23578579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibson A. P., Austin T., Everdell N. L., Schweiger M., Arridge S. R., Meek J. H., Wyatt J. S., Delpy D. T., Hebden J. C., “Three-dimensional whole-head optical tomography of passive motor evoked responses in the neonate,” Neuroimage 30(2), 521–528 (2006).10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.08.059 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
