Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults
- PMID: 21412914
- PMCID: PMC4171034
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub2
Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults
Update in
-
Gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Apr 27;2014(4):CD007938. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 09;6:CD007938. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007938.pub4. PMID: 24771480 Free PMC article. Updated.
Abstract
Background: This review updates parts of two earlier Cochrane reviews investigating effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). Antiepileptic drugs are used to manage pain, predominantly for chronic neuropathic pain, especially when the pain is lancinating or burning.
Objectives: To evaluate the analgesic effectiveness and adverse effects of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain management.
Search strategy: We identified randomised trials of gabapentin in acute, chronic or cancer pain from MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL. We obtained clinical trial reports and synopses of published and unpublished studies from Internet sources. The date of the most recent search was January 2011.
Selection criteria: Randomised, double-blind studies reporting the analgesic and adverse effects of gabapentin in neuropathic pain with assessment of pain intensity and/or pain relief, using validated scales. Participants were adults aged 18 and over.
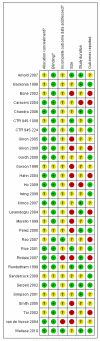
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data. We calculated numbers needed to treat to benefit (NNTs), concentrating on IMMPACT (Initiative on Methods, Measurement and Pain Assessment in Clinical Trials) definitions of at least moderate and substantial benefit, and to harm (NNH) for adverse effects and withdrawal. Meta-analysis was undertaken using a fixed-effect model.
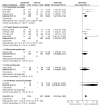
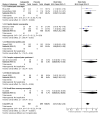
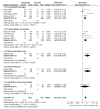
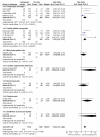
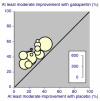
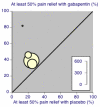
Main results: Twenty-nine studies (3571 participants), studied gabapentin at daily doses of 1200 mg or more in 12 chronic pain conditions; 78% of participants were in studies of postherpetic neuralgia, painful diabetic neuropathy or mixed neuropathic pain. Using the IMMPACT definition of at least moderate benefit, gabapentin was superior to placebo in 14 studies with 2831 participants, 43% improving with gabapentin and 26% with placebo; the NNT was 5.8 (4.8 to 7.2). Using the IMMPACT definition of substantial benefit, gabapentin was superior to placebo in 13 studies with 2627 participants, 31% improving with gabapentin and 17% with placebo; the NNT was 6.8 (5.6 to 8.7). These estimates of efficacy are more conservative than those reported in a previous review. Data from few studies and participants were available for other painful conditions.Adverse events occurred significantly more often with gabapentin. Persons taking gabapentin can expect to have at least one adverse event (66%), withdraw because of an adverse event (12%), suffer dizziness (21%), somnolence (16%), peripheral oedema (8%), and gait disturbance (9%). Serious adverse events (4%) were no more common than with placebo.There were insufficient data for comparisons with other active treatments.
Authors' conclusions: Gabapentin provides pain relief of a high level in about a third of people who take if for painful neuropathic pain. Adverse events are frequent, but mostly tolerable. More conservative estimates of efficacy resulted from using better definitions of efficacy outcome at higher, clinically important, levels, combined with a considerable increase in the numbers of studies and participants available for analysis.
Figures
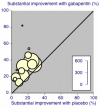
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: Gabapentin reduces some types of chronic neuropathic pain more than placebo in adults.Ann Intern Med. 2011 Jul 19;155(2):JC1-8. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-155-2-201107190-02008. Ann Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 21768574 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
-
- Arnold LM, Goldenberg DL, Stanford SB, Lalonde JK, Sandhu HS, Keck PE, Jr, et al. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2007;56(4):1336–44. [DOI: 10.1002/art.22457] - PubMed
-
-
*
- Backonja M, Beydoun A, Edwards KR, Schwartz SL, Fonseca V, Hes M, et al. Gabapentin for the symptomatic treatment of painful neuropathy in patients with diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 1998;280(21):1831–6. [PUBMED: 9846777] - PubMed
-
Trial summary - Parke Davis/Pfizer 945-210. Unpublished report.
-
-
- Bone M, Critchley P, Buggy DJ. Gabapentin in postamputation phantom limb pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over study. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine. 2002;27(5):481–6. [DOI: 10.1053/rapm.2002.35169] - PubMed
-
- Caraceni A, Zecca E, Bonezzi C, Arcuri E, Yaya Tur R, et al. Gabapentin for neuropathic cancer pain: a randomized controlled trial from the Gabapentin Cancer Pain Study Group. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2004;22(14):2909–17. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2004.08.141] - PubMed
-
- Chandra K, Shafiq N, Pandhi P, Gupta S, Malhotra S. Gabapentin versus nortriptyline in post-herpetic neuralgia patients: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial - the GONIP Trial. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2006;44(8):358–63. [PUBMED: 16961166] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
-
- Arai YC, Matsubara T, Shimo K, Suetomi K, Nishihara M, Ushida T, et al. Low-dose gabapentin as useful adjuvant to opioids for neuropathic cancer pain when combined with low-dose imipramine. Journal of Anesthesia. 2010;24(3):407–10. [DOI: 10.1007/s00540-010-0913-6] - PubMed
-
- Berry JD, Petersen KL. A single dose of gabapentin reduces acute pain and allodynia in patients with herpes zoster. Neurology. 2005;65(3):444–7. [PUBMED: 16087911] - PubMed
-
- Dallocchio C, Buffa C, Mazzarello P, Chiroli S. Gabapentin vs. amitriptyline in painful diabetic neuropathy: an open-label pilot study. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2000;20(4):280–5. [DOI: 10.1016/S0885-3924 (00)00181-0] - PubMed
-
- Dworkin RH, Barbano RL, Tyring SK, Betts RF, McDermott MP, Pennella-Vaughan J, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of oxycodone and of gabapentin for acute pain in herpes zoster. Pain. 2009;142(3):209–17. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2008.12.022] - PubMed
-
- Jean WH, Wu CC, Mok MS, Sun WZ. Starting dose of gabapentin for patients with post-herpetic neuralgia--a dose-response study. Acta Anaesthesiologica Taiwan. 2005;43(2):73–7. [PUBMED: 16060401] - PubMed
Additional references
-
- Bouhassira D, Lant?ri-Minet M, Attal N, Laurent B, Touboul C. Prevalence of chronic pain with neuropathic characteristics in the general population. Pain. 2008;136(3):380–7. - PubMed
-
- Breivik H, Collett B, Ventafridda V, Cohen R, Gallacher D. Survey of chronic pain in Europe: prevalence, impact on daily life, and treatment. European Journal of Pain. 2006;10(4):287–333. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2005.06.009] - PubMed
-
- Chou R, Carson S, Chan BK. Gabapentin versus tricyclic antidepressants for diabetic neuropathy and post-herpetic neuralgia: discrepancies between direct and indirect meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2009;24(2):178–88. [DOI: 10.1007/ s11606-008-0877-5] - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

