Chronic assessment of diaphragm muscle EMG activity across motor behaviors
- PMID: 21414423
- PMCID: PMC3103648
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.03.011
Chronic assessment of diaphragm muscle EMG activity across motor behaviors
Abstract
The diaphragm muscle is the main inspiratory muscle in mammals. Quantitative analyses documenting the reliability of chronic diaphragm EMG recordings are lacking. Assessment of ventilatory and non-ventilatory motor behaviors may facilitate evaluating diaphragm EMG activity over time. We hypothesized that normalization of diaphragm EMG amplitude across behaviors provides stable and reliable parameters for longitudinal assessments of diaphragm activity. We found that diaphragm EMG activity shows substantial intra-animal variability over 6 weeks, with coefficient of variation (CV) for different behaviors ∼ 29-42%. Normalization of diaphragm EMG activity to near maximal behaviors (e.g., deep breathing) reduced intra-animal variability over time (CV ∼ 22-29%). Plethysmographic measurements of eupneic ventilation were also stable over 6 weeks (CV ∼ 13% for minute ventilation). Thus, stable and reliable measurements of diaphragm EMG activity can be obtained longitudinally using chronically implanted electrodes by examining multiple motor behaviors. By quantitatively determining the reliability of longitudinal diaphragm EMG analyses, we provide an important tool for evaluating the progression of diseases or injuries that impair ventilation.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
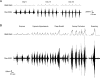
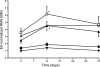
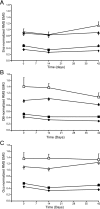
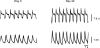
References
-
- Alford EK, Roy RR, Hodgson JA, Edgerton VR. Electromyography of rat soleus, medial gastrocnemius, and tibialis anterior during hind limb suspension. Exp. Neurol. 1987;96:635–649. - PubMed
-
- Bell HJ, Haouzi P. The hypoxia-induced facilitation of augmented breaths is suppressed by the common effect of carbonic anhydrase inhibition. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2010;171:201–211. - PubMed
-
- Blewett C, Elder GC. Quantitative EMG analysis in soleus and plantaris during hindlimb suspension and recovery. J. Appl. Physiol. 1993;74:2057–2066. - PubMed
-
- Bolcskei K, Tekus V, Dezsi L, Szolcsanyi J, Petho G. Antinociceptive desensitizing actions of TRPV1 receptor agonists capsaicin, resiniferatoxin and N-oleoyldopamine as measured by determination of the noxious heat and cold thresholds in the rat. Eur. J. Pain. 2010;14:480–486. - PubMed
-
- Chang FC, Harper RM. A procedure for chronic recording of diaphragmatic electromyographic activity. Brain Res. Bull. 1989;22:561–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

