Cellular decision making and biological noise: from microbes to mammals
- PMID: 21414483
- PMCID: PMC3068611
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.030
Cellular decision making and biological noise: from microbes to mammals
Abstract
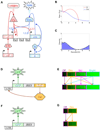
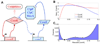
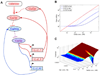
Cellular decision making is the process whereby cells assume different, functionally important and heritable fates without an associated genetic or environmental difference. Such stochastic cell fate decisions generate nongenetic cellular diversity, which may be critical for metazoan development as well as optimized microbial resource utilization and survival in a fluctuating, frequently stressful environment. Here, we review several examples of cellular decision making from viruses, bacteria, yeast, lower metazoans, and mammals, highlighting the role of regulatory network structure and molecular noise. We propose that cellular decision making is one of at least three key processes underlying development at various scales of biological organization.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

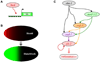
References
-
- Acar M, Becskei A, van Oudenaarden A. Enhancement of cellular memory by reducing stochastic transitions. Nature. 2005;435:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Acar M, Mettetal JT, van Oudenaarden A. Stochastic switching as a survival strategy in fluctuating environments. Nat Genet. 2008;40:471–475. - PubMed
-
- Arias AM, Hayward P. Filtering transcriptional noise during development: concepts and mechanisms. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:34–44. - PubMed
-
- Balaban NQ, Merrin J, Chait R, Kowalik L, Leibler S. Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch. Science. 2004;305:1622–1625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

