Phase-transfer energetics of small-molecule alcohols across the water-hexane interface: molecular dynamics simulations using charge equilibration models
- PMID: 21414823
- PMCID: PMC3070209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2010.09.005
Phase-transfer energetics of small-molecule alcohols across the water-hexane interface: molecular dynamics simulations using charge equilibration models
Abstract
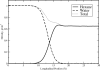
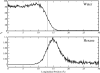
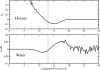
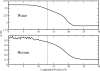
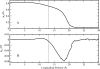
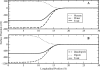
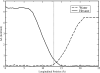
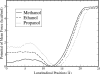
We study the water-hexane interface using molecular dynamics (MD) and polarizable charge equilibration (CHEQ) force fields. Bulk densities for TIP4P-FQ water and hexane, 1.0086±0.0002 and 0.6378±0.0001 g/cm(3), demonstrate excellent agreement with experiment. Interfacial width and interfacial tension are consistent with previously reported values. The in-plane component of the dielectric permittivity (ɛ(||)) for water is shown to decrease from 81.7±0.04 to unity, transitioning longitudinally from bulk water to bulk hexane. ɛ(||) for hexane reaches a maximum in the interface, but this term represents only a small contribution to the total dielectric constant (as expected for a non-polar species). Structurally, net orientations of the molecules arise in the interfacial region such that hexane lies slightly parallel to the interface and water reorients to maximize hydrogen bonding. Interfacial potentials due to contributions of the water and hexane are calculated to be -567.9±0.13 and 198.7±0.01 mV, respectively, giving rise to a total potential in agreement with the range of values reported from previous simulations of similar systems. Potentials of mean force (PMF) calculated for methanol, ethanol, and 1-propanol for the transfer from water to hexane indicate an interfacial free energy minimum, corresponding to the amphiphilic nature of the molecules. The magnitudes of transfer free energies were further characterized from the solvation free energies of alcohols in water and hexane using thermodynamic integration. This analysis shows that solvation free energies for alcohols in hexane are 0.2-0.3 kcal/mol too unfavorable, whereas solvation of alcohols in water is approximately 1 kcal/mol too favorable. For the pure hexane-water interfacial simulations, we observe a monotonic decrease of the water dipole moment to near-vacuum values. This suggests that the electrostatic component of the desolvation free energy is not as severe for polarizable models than for fixed-charge force fields. The implications of such behavior pertain to the modeling of polar and charged solutes in lipidic environments.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interfacial structure, thermodynamics, and electrostatics of aqueous methanol solutions via molecular dynamics simulations using charge equilibration models.J Phys Chem B. 2009 Jul 9;113(27):9241-54. doi: 10.1021/jp900446f. J Phys Chem B. 2009. PMID: 19569724 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the hexane-water interface via molecular dynamics simulations using nonadditive alkane-water potentials.J Chem Phys. 2006 May 28;124(20):204706. doi: 10.1063/1.2198538. J Chem Phys. 2006. PMID: 16774363
-
Halothane solvation in water and organic solvents from molecular simulations with new polarizable potential function.J Phys Chem B. 2010 May 20;114(19):6401-8. doi: 10.1021/jp908339j. J Phys Chem B. 2010. PMID: 20411978
-
Accounting for electronic polarization in non-polarizable force fields.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011 Feb 21;13(7):2613-26. doi: 10.1039/c0cp01971b. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 21212894 Review.
-
Influence of alkane and perfluorocarbon vapors on adsorbed surface layers and spread insoluble monolayers of surfactants, proteins and lipids.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Jun;244:100-112. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2015.11.004. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 26656422 Review.
References
-
- Bard AJ, Faulkner LR. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applicatioins. Wiley; New York: 1980.
-
- Haslam S, et al. Surface second harmonic generation studies of the dodecane/water interface: the equilibrium and kinetic behavior of p-nitrophenol and tri-n-butyl phosphate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000;2:3235–3245.
-
- Wilson MA, Pohorille A. Molecular Dynamics of a Water-Lipid Bilayer Interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994;116:1490–1501. - PubMed
-
- Ly HV, Block DE, Longo ML. Interfacial tension effect on lipid bilayer rigidity, stability, and area/molecule: a micropipette aspiration approach. Langmuir. 2002;18:8988.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

