Conformational flexibility of the ligand-binding domain dimer in kainate receptor gating and desensitization
- PMID: 21414913
- PMCID: PMC6623771
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4771-10.2011
Conformational flexibility of the ligand-binding domain dimer in kainate receptor gating and desensitization
Abstract
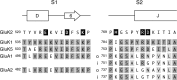
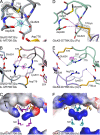
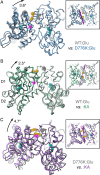
AMPA- and kainate (KA)-selective ionotropic glutamate receptors (iGluRs) respond to agonist by opening (gating), then closing (desensitizing) in quick succession. Gating has been linked to agonist-induced changes within the ligand-binding domain (LBD), and desensitization to rearrangement of a dimer formed by neighboring LBDs. To explore the role of dimer conformation in both gating and desensitization, we compared the conformational effects of two kainate receptor mutants. The first, GluK2-D776K, blocks desensitization of macroscopic current responses ("macroscopic desensitization"). The second, GluK2-M770K, accelerates macroscopic desensitization and eliminates the effects of external ions on channel kinetics. Using structures determined by x-ray crystallography, we found that in both mutants the introduced lysines act as tethered cations, displacing sodium ions from their binding sites within the dimer interface. This results in new inter- and intra-protomer contacts in D776K and M770K respectively, explaining the effects of these mutations on dimer stability and desensitization kinetics. Further, chloride binding was unaffected by the M770K mutation, even though binding of sodium ions has been proposed to promote dimer stability by stabilizing anion binding. This suggests sodium binding may affect receptor function more directly than currently supposed. Notably, we also observed a ligand-specific shift in dimer conformation when comparing LBD dimers in complex with glutamate or the partial agonist KA, revealing a previously unidentified role for dimer orientation in iGluR gating.
Figures


References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2002;58:1948–1954. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Gouaux E. Mechanisms for activation and antagonism of an AMPA-sensitive glutamate receptor: crystal structures of the GluR2 ligand binding core. Neuron. 2000;28:165–181. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong N, Jasti J, Beich-Frandsen M, Gouaux E. Measurement of conformational changes accompanying desensitization in an ionotropic glutamate receptor. Cell. 2006;127:85–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
