Sleep and activity in chronic kidney disease: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 21415310
- PMCID: PMC3109920
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10581110
Sleep and activity in chronic kidney disease: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Background and objectives: Commonly sleep is disrupted and physical activity is restricted among patients with CKD and those on long-term dialysis. However, few studies have assessed patients longitudinally.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: We compared the prevalence of sleep disturbances measured both subjectively using a questionnaire and objectively using actimetry among patients with CKD (n = 145), those on hemodialysis (n = 116), and people without kidney disease (n = 19). Activity level during the day was measured using actimetry, and patients were then followed for up to 2 years.
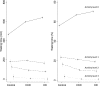
Results: Compared with people without kidney disease, patients with CKD not on dialysis had disruption of sleep that was independent of several risk factors. However, disrupted sleep was correlated with neither estimated GFR in cross-sectional nor longitudinal assessment. Those on hemodialysis had sleep disruption that was of much greater severity than that found among those with CKD not on dialysis. Furthermore, missing or shortening the prescribed duration of dialysis was associated with greater severity of sleep disturbance in cross-sectional but not in longitudinal assessment. Day-time activity declined both in duration and intensity from controls to CKD to hemodialysis.
Conclusions: The loss of kidney function is related to both reduced duration and intensity of day time physical activity. Although patients with CKD have disrupted sleep, this is independent of estimated GFR. However, compared with those with CKD, dialysis patients have more severely disrupted sleep; this is related to missing dialysis. Thus, shortening patients' dialysis may reduce their sleep.
Figures
References
-
- Parker KP, Bliwise DL, Bailey JL, Rye DB: Polysomnographic measures of nocturnal sleep in patients on chronic, intermittent daytime haemodialysis vs those with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20: 1422–1428, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Kurella M, Luan J, Lash JP, Chertow GM: Self-assessed sleep quality in chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 37: 159–165, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Hanly PJ, Pierratos A: Improvement of sleep apnea in patients with chronic renal failure who undergo nocturnal hemodialysis. N Engl J Med 344: 102–107, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Beecroft JM, Hoffstein V, Pierratos A, Chan CT, McFarlane P, Hanly PJ: Nocturnal haemodialysis increases pharyngeal size in patients with sleep apnoea and end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23: 673–679, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

