SDF-1α induction in mature smooth muscle cells by inactivation of PTEN is a critical mediator of exacerbated injury-induced neointima formation
- PMID: 21415388
- PMCID: PMC3111081
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.223701
SDF-1α induction in mature smooth muscle cells by inactivation of PTEN is a critical mediator of exacerbated injury-induced neointima formation
Abstract
Objective: PTEN inactivation selectively in smooth muscle cells (SMC) initiates multiple downstream events driving neointima formation, including SMC cytokine/chemokine production, in particular stromal cell-derived factor-1α (SDF-1α). We investigated the effects of SDF-1α on resident SMC and bone marrow-derived cells and in mediating neointima formation.
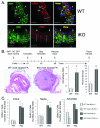
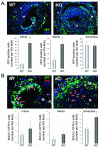
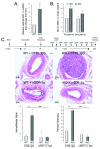
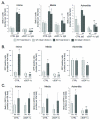
Methods and results: Inducible, SMC-specific PTEN knockout mice (PTEN iKO) were bred to floxed-stop ROSA26-β-galactosidase (βGal) mice to fate-map mature SMC in response to injury; mice received wild-type green fluorescent protein-labeled bone marrow to track recruitment. Following wire-induced femoral artery injury, βGal(+) SMC accumulated in the intima and adventitia. Compared with wild-type, PTEN iKO mice exhibited massive neointima formation, increased replicating intimal and medial βGal(+)SMC, and enhanced vascular recruitment of bone marrow cells following injury. Inhibiting SDF-1α blocked these events and reversed enhanced neointima formation observed in PTEN iKO mice. Most recruited green fluorescent protein(+) cells stained positive for macrophage markers but not SMC markers. SMC-macrophage interactions resulted in a persistent SMC inflammatory phenotype that was dependent on SMC PTEN and SDF-1α expression.
Conclusion: Resident SMC play a multifaceted role in neointima formation by contributing the majority of neointimal cells, regulating recruitment of inflammatory cells, and contributing to adventitial remodeling. The SMC PTEN-SDF-1α axis is a critical regulator of these events.
Figures

References
-
- Owens GK, Kumar MS, Wamhoff BR. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:767–801. - PubMed
-
- Schober A. Chemokines in vascular dysfunction and remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:1950–1959. - PubMed
-
- Clowes AW, Reidy MA, Clowes MM. Kinetics of cellular proliferation after arterial injury. I. Smooth muscle growth in the absence of endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983;49:327–333. - PubMed
-
- Imai H, Lee KJ, Lee SK, Lee KT, O’Neal RM, Thomas WA. Ultrastructural features of aortic cells in mitosis in control and cholesterol-fed swine. Lab Invest. 1970;23:401–415. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

