Themes in fibrosis and gastrointestinal inflammation
- PMID: 21415411
- PMCID: PMC3094134
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00104.2011
Themes in fibrosis and gastrointestinal inflammation
Abstract
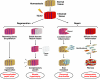
Wound healing is an appropriate response to inflammation and tissue injury in the gastrointestinal tract. If wound healing responses are excessive, perpetuated, or prolonged, they lead to fibrosis, distortion of tissue architecture, and loss of function. This introductory editorial and the minireviews or reviews in this themes series highlight the diversity in severity and location of fibrosis in response to gastrointestinal inflammation. The multiplicity of cellular and molecular mediators and new players, including stem cells or extracellular matrix-producing cells derived from nonmesenchymal cell types, is reviewed. Comparisons of inflammation-induced fibrosis across organ systems and the need for integrated and systems-based molecular approaches, new imaging modalities, well-characterized animal models, cell culture models, and improved diagnostic or predictive markers are reviewed. To date, intestinal fibrosis has received much less attention than inflammation in terms of defining mechanisms and underlying causes. This themes series aims to illustrate the importance of research in this area in gastrointestinal health and disease.
Figures
References
-
- Aceves SS, Newbury RO, Dohil R, Bastian JF, Broide DH. Esophageal remodeling in pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 119: 206–212, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Andoh A, Zhang Z, Inatomi O, Fujino S, Deguchi Y, Araki Y, Tsujikawa T, Kitoh K, Kim-Mitsuyama S, Takayanagi A, Shimizu N, Fujiyama Y. Interleukin-22, a member of the IL-10 subfamily, induces inflammatory responses in colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts. Gastroenterology 129: 969–984, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Atherton JC. The pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori-induced gastro-duodenal diseases. Annu Rev Pathol 1: 63–96, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Baltimore D, Boldin MP, O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Taganov KD. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat Immunol 9: 839–845, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

