Medical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 21415957
- PMCID: PMC3033123
- DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2009.021
Medical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
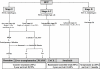
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common neoplasm and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Cirrhosis, most often due to viral hepatitis, is the predominant risk factors for HCC and geographical differences in both risk factors and incidence are largely due to epidemiological variations in hepatitis B and C infection. Hepatic function is a relevant parameter in selecting therapy in HCC. The current clinical classification of HCC split patients into 5 stages, with a specific treatment schedule for any stage. As patients with early stages can receive curative treatments, such as surgical resection, liver transplantation or local ablation, surveillance program in high-risk populations has become mandatory. Sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor, has recently shown survival benefits in patients at advanced stage of disease. Hopefully, new molecular targeted therapies and their combination with sorafenib or interventional and surgical procedures, should expand the therapeutic armamentarium against HCC.
Figures
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Sangiovanni A, Del Ninno E, Fasani P, De Fazio C, Ronchi G, Romeo R, Morabito A, De Franchis R, Colombo M. Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with a hepatocellular carcinoma detected during surveillance. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:1005–14. - PubMed
-
- Beasley RP, Hwang LY, Lin CC, Chien CS. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981;2:1129–33. - PubMed
-
- Fattovich G, McIntyre G, Thursz M, Colman K, Giuliano G, Alberti A, Thomas HC, Carman WF. Hepatitis B virus precore/core variation and interferon therapy. Hepatology. 1995;22:1355–62. 2:1129–33. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Sherman M. Diagnosis of Small HCC. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:1364. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials