Nowcasting pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 hospitalizations in the Netherlands
- PMID: 21416274
- PMCID: PMC3079092
- DOI: 10.1007/s10654-011-9566-5
Nowcasting pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 hospitalizations in the Netherlands
Abstract
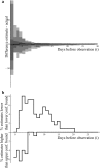
During emerging epidemics of infectious diseases, it is vital to have up-to-date information on epidemic trends, such as incidence or health care demand, because hospitals and intensive care units have limited excess capacity. However, real-time tracking of epidemics is difficult, because of the inherent delay between onset of symptoms or hospitalizations, and reporting. We propose a robust algorithm to correct for reporting delays, using the observed distribution of reporting delays. We apply the algorithm to pandemic influenza A/H1N1 2009 hospitalizations as reported in the Netherlands. We show that the proposed algorithm is able to provide unbiased predictions of the actual number of hospitalizations in real-time during the ascent and descent of the epidemic. The real-time predictions of admissions are useful to adjust planning in hospitals to avoid exceeding their capacity.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

