miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and is down-regulated in gastric cancer
- PMID: 21418558
- PMCID: PMC3070685
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-29
miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and is down-regulated in gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer is the fourth most common cancer in the world and the second most prevalent cause of cancer related death. The development of gastric cancer is mainly associated with H. Pylori infection leading to a focus in pathology studies on bacterial and environmental factors, and to a lesser extent on the mechanistic development of the tumour. MicroRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules involved in post-transcriptional gene regulation. They are found to regulate genes involved in diverse biological functions and alterations in microRNA expression have been linked to the pathogenesis of many malignancies. The current study is focused on identifying microRNAs involved in gastric carcinogenesis and to explore their mechanistic relevance by characterizing their targets.
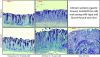
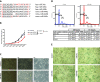
Results: Invitrogen NCode miRNA microarrays identified miR-449 to be decreased in 1-year-old Gastrin KO mice and in H. Pylori infected gastric tissues compared to tissues from wild type animals. Growth rate of gastric cell lines over-expressing miR-449 was inhibited by 60% compared to controls. FACS cell cycle analysis of miR-449 over-expressing cells showed a significant increase in the sub-G1 fraction indicative of apoptosis. ß-Gal assays indicated a senescent phenotype of gastric cell lines over-expressing miR-449. Affymetrix 133v2 arrays identified GMNN, MET, CCNE2, SIRT1 and CDK6 as miR-449 targets. Luciferase assays were used to confirm GMNN, MET, CCNE2 and SIRT1 as direct targets. We also show that miR-449 over-expression activated p53 and its downstream target p21 as well as the apoptosis markers cleaved CASP3 and PARP. Importantly, qPCR analyses showed a loss of miR-449 expression in human clinical gastric tumours compared to normal tissues.
Conclusions: In this study, we document a diminished expression of miR-449 in Gastrin KO mice and further confirmed its loss in human gastric tumours. We investigated the function of miR-449 by identifying its direct targets. Furthermore we show that miR-449 induces senescence and apoptosis by activating the p53 pathway.
Figures



References
-
- Wang TC, Dangler CA, Chen D, Goldenring JR, Koh T, Raychowdhury R, Coffey RJ, Ito S, Varro A, Dockray GJ, Fox JG. Synergistic interaction between hypergastrinemia and Helicobacter infection in a mouse model of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:36–47. doi: 10.1016/S0016-5085(00)70412-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takaishi S, Tu S, Dubeykovskaya ZA, Whary MT, Muthupalani S, Rickman BH, Rogers AB, Lertkowit N, Varro A, Fox JG, Wang TC. Gastrin is an essential cofactor for helicobacter-associated gastric corpus carcinogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. Am J Pathol. 2009;175:365–375. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.081165. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

