Synthesis and biological evaluation of new 2-alkylaminoethyl-1,1-bisphosphonic acids against Trypanosoma cruzi and Toxoplasma gondii targeting farnesyl diphosphate synthase
- PMID: 21419634
- PMCID: PMC3071284
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.02.037
Synthesis and biological evaluation of new 2-alkylaminoethyl-1,1-bisphosphonic acids against Trypanosoma cruzi and Toxoplasma gondii targeting farnesyl diphosphate synthase
Abstract
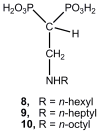
The effect of long-chain 2-alkylaminoethyl-1,1-bisphosphonates against proliferation of the clinically more relevant form of Trypanosoma cruzi, the etiologic agent of American trypanosomiasis (Chagas' disease), and against tachyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii was investigated. Particularly, compound 26 proved to be an extremely potent inhibitor against the intracellular form of T. cruzi, exhibiting IC(50) values at the nanomolar range. This cellular activity was associated with a strong inhibition of the enzymatic activity of T. cruzi farnesyl diphosphate synthase (TcFPPS), which constitutes a valid target for Chagas' disease chemotherapy. Compound 26 was an effective agent against T. cruzi (amastigotes) exhibiting an IC(50) value of 0.67 μM, while this compound showed an IC(50) value of 0.81 μM against the target enzyme TcFPPS. This drug was less effective against the enzymatic activity of T. cruzi solanesyl diphosphate synthase TcSPPS showing an IC(50) value of 3.2 μM. Interestingly, compound 26 was also very effective against T. gondii (tachyzoites) exhibiting IC(50) values of 6.23 μM. This cellular activity was also related to the inhibition of the enzymatic activity towards the target enzyme TgFPPS (IC(50)=0.093 μM) As bisphosphonate-containing compounds are FDA-approved drugs for the treatment of bone resorption disorders, their potential low toxicity makes them good candidates to control different tropical diseases.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-alkylaminoethyl-1,1-bisphosphonic acids against Trypanosoma cruzi and Toxoplasma gondii targeting farnesyl diphosphate synthase.Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Mar 15;16(6):3283-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.12.010. Epub 2007 Dec 10. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18096393 Free PMC article.
-
1-(Fluoroalkylidene)-1,1-bisphosphonic acids are potent and selective inhibitors of the enzymatic activity of Toxoplasma gondii farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase.Org Biomol Chem. 2012 Feb 21;10(7):1424-33. doi: 10.1039/c1ob06602a. Epub 2012 Jan 3. Org Biomol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22215028 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of sulfur-containing 1,1-bisphosphonic acids as antiparasitic agents.Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Feb;60:431-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2012.12.015. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Eur J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23318904 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches for Designing new Potent Inhibitors of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016;11(3):307-20. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2016.1143814. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 26781029 Review.
-
New therapeutic targets for drug design against Trypanosoma cruzi, advances and perspectives.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(25):3286-93. doi: 10.2174/092986709788803303. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19548870 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis of Amino-gem-Bisphosphonate Derivatives and Their Application as Synthons for the Preparation of Biorelevant Compounds.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;18(7):1063. doi: 10.3390/ph18071063. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Experimental Compounds Demonstrating Anti-Toxoplasma Activity.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Nov 21;60(12):7017-7034. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01176-16. Print 2016 Dec. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27600037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-alkylaminomethyl-1,1-bisphosphonic acids against Trypanosoma cruzi and Toxoplasma gondii.Bioorg Med Chem. 2019 Aug 15;27(16):3663-3673. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2019.07.004. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Bioorg Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31296439 Free PMC article.
-
Antiparasitic Activity of Sulfur- and Fluorine-Containing Bisphosphonates against Trypanosomatids and Apicomplexan Parasites.Molecules. 2017 Jan 4;22(1):82. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010082. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28054995 Free PMC article.
-
Triazole-based compound as a candidate to develop novel medicines to treat toxoplasmosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Dec;58(12):7583-5. doi: 10.1128/AAC.03832-14. Epub 2014 Oct 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 25288090 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

